What is a Wireless Channel?

Quick Definition: Wireless channels are specific frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are made of several channels and are used to transmit data wirelessly. Wireless channels are allocated for Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks.
Wireless channels are everywhere. Whether you're chatting on a cell phone, browsing social media on Wi-Fi, or listening to music via Bluetooth, wireless channels have got you covered. As you can see, its widespread use (and importance for Network+) makes mastery essential. Its ubiquitousness also entails a lot of regulatory compliance. Don't worry, though, we'll cover that too.
Let's first define wireless channels. Then, we'll walk through some of the compliance requirements before tackling installation.
What are Wireless Channels in Networking?
Wireless channels are the medium through which wireless communication signals are transmitted. To understand wireless channels, think back to the last time you watched TV. Each channel represents a different station, and each channel serves a different purpose. For example, you have the Weather Channel, Comedy Central, and QVC.
In wireless channels, each "TV channel" represents a different channel on the frequency. So, for wireless channels, cell phones, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi would belong on a different TV channel. It's really that simple: wireless channels are specific frequencies used to exchange and send data. Just like how a TV operates on different channels, radio frequencies do, too.
Wireless channels are mainly for Bluetooth, cell phones, and Wi-Fi. Each technology operates on a separate frequency. Let's list each of them and their frequencies.
Bluetooth is a short-range connectivity technology. For example, it connects AirPods to iPhones. It operates in the 2.4 GHz band, though it does use "bandwidth hopping" to increase fidelity.
Cell phones operate on a wide range of channels, such as 700, 1800, and 2400 MHz. Also, the all too familiar 5G network is also its own frequency band. 5G operates below 6 GHz. Frequency allocation is often assigned to different carriers. (AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile, etc.) That has more to do with regulation, which we'll cover shortly.
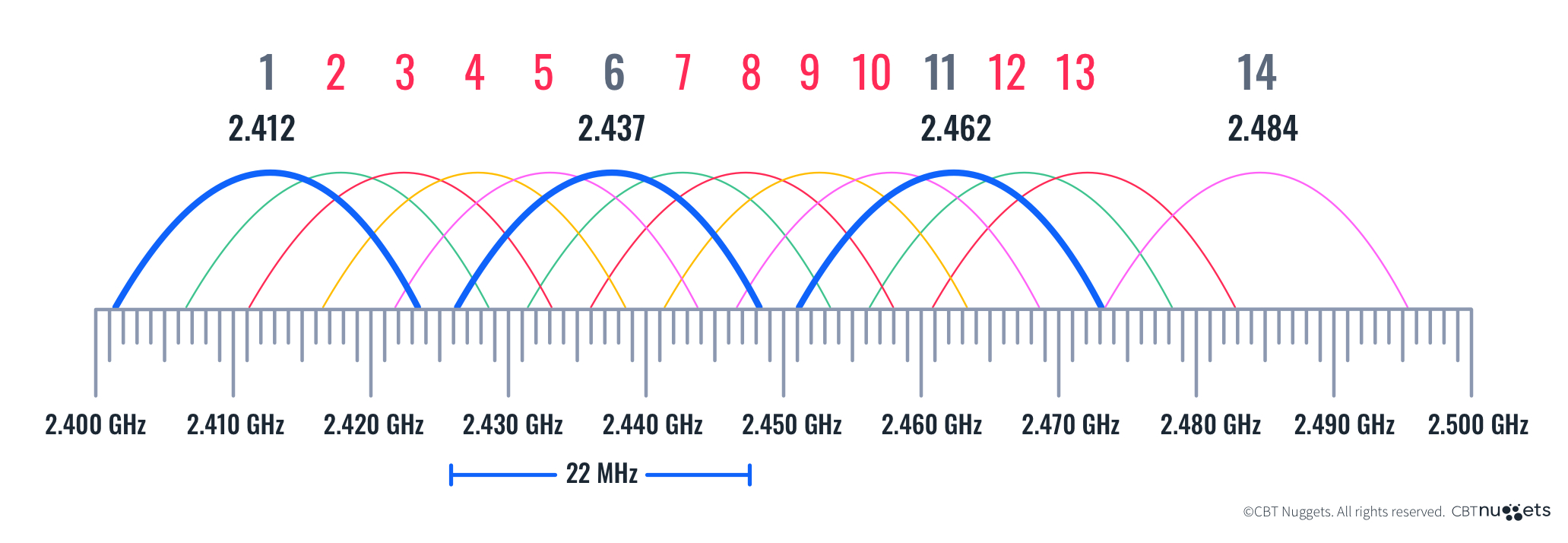
Wi-Fi is the bread and butter of modern-day internet access. Wi-Fi uses frequency channels to send binary data to and from NIC-enabled devices. Wi-Fi functions on two main frequencies: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Wi-Fi 6E introduces a third frequency: 6 GHz.
With all that in mind, let's cover the regulatory compliance associated with wireless channels. After all, there are a LOT of organizations surfing these frequency bands, and we'll discover how they do so without impediments.
What are the Regulatory Impacts on Wireless Standards?
The regulatory impact on wireless channels is wide and vast. The ITU (International Telecommunication Union) creates and mandates all these Kafkaesque regulations internationally, and the FCC enforces them here in the US.
The FCC was founded in 1934 to regulate the new-fangled radio. Its key roles are radio frequency licensure, rulemaking, and enforcing said rules. As frequencies expanded to include Wi-Fi, cell phones, and Bluetooth, so did the FCC's responsibilities. Bearing that in mind, let's walk through some of the legal requirements on wireless channels.
Legal Requirements and Standards for Wireless Technologies
Legal requirements are vital to ensure the efficiency, safety, and access to wireless channels. For wireless channels, one of the most important FCC requirements is frequency auctions. Governments often auction frequency bands to commercial entities. As with any other auction, the highest bidder acquires the frequency rights. These bidders are often ISPs, broadcasters, or cell phone providers.
The FCC does far more than throw auction parties. It also ensures the safe usage of high-frequency equipment. For example, the FCC makes sure cell phone towers transmit at the correct wireless channel ranges. It's important that ISPs don't use dangerous frequencies, which could break equipment or interfere with airplanes. The FCC provides detailed rules and regulations to prevent this.
A third important aspect to consider is spectrum regulations and limits. For example, certain wireless channels have regulations that only allow their use in emergencies. In the US, the 700 MHz band is used for public broadcasting emergencies. Some channels focus exclusively on astronomy and scientific endeavors. An astronomer doesn't want to hear a cell phone conversation while he's counting craters on Mars.
Lastly, the FCC grants exclusive rights to different providers to use wireless channels. Think back to the TV analogy. It'd be pretty weird if channel 42 were one day Nickelodeon and the next day the Home & Gardening Channel. The FCC reserves wireless channels like TV channels—one user per band.
Regulatory Compliance Challenges
No one understands regulatory challenges quite like ISPs and cell phone providers. There's a glut of regulations to adhere to, and it can be hard to track. This is particularly true when dealing with region-to-region traffic. One of the most difficult aspects of region-to-region is complying with state and local restrictions. This burdensome process can often stymie development, such as 5G towers and cell phone coverage.
Other challenges stem from fines imposed via FCC violations. Exceeding power limits or using unauthorized bands can lead to substantial fees. Companies may need to hire attorneys to appeal the fines. The appellate process can cause the project to halt until litigation reaches its conclusion.
Staying up to date with the latest compliance requirements is critical. The fluidity of regulation change requires a proactive approach. Each organization has a team that monitors and communicates with the FCC to ensure timely adherence to the latest requests. It's not uncommon for organizations to hold training sessions on new regulations that will affect their employees.
Now that we've gone over compliance let's talk about wireless channel installation with compliance in mind.
How to Install and Configure Wireless Devices for Compliance
Installing a wireless device is an exciting but challenging opportunity. It's important to adhere to all FCC compliance to ensure efficiency, security, and reliability. Let's go over some high-level considerations before tackling the project.
"Wireless device" is pretty broad. It can mean anything from an antenna to a modem to a cell phone base station. In most situations, you'll follow these broad guidelines.
Pre-Install Considerations
Carefully review all national, state, and local regulations and requirements. Visit the FCC website and review the frequency allocation table to see the correct wavelength for your region.
Study the technical standards and compliance requirements set by the regulatory authority. Examples include power limits, permissible frequencies, and emission standards.
Installation process
Next, verify that the equipment meets technical compliance with FCC guidelines. The vendor documentation will outline certification details.
When installing the device, ensure it complies with FCC guidelines. Check the vendor documentation for certification details. Confirm that the equipment is suitable for the task. The frequency bands must align with your region's frequency table.
If installing antennas, position them to minimize interference with other devices and to provide the maximum amount of coverage possible for the intended area.
An antenna takes up a lot of power. Ensure that you adhere to environmental regulations on power consumption. Also, you can use different power settings for various environments, such as urban or rural. Consult the vendor's documentation to confirm the appropriate power mode.
Security Considerations
The next thing to think about is security. Nothing is worth doing if it is not done securely. It's a good idea to enable strong encryption protocols. WPA3, for example, is a commonplace encryption mechanism for wireless transmission. Regularly update and manage encryption keys to ensure they don't go out of date or expire.
What are the Best Practices for Maintaining Compliance?
Maintaining compliance does not have to be an arduous process. By following the steps outlined below, you'll be sure to mitigate nasty surprises. Not only that, you'll bring your stress down to (just barely) acceptable levels.
Conduct Regular Audits
Nothing makes managers happier than thorough and regular audits. Here are a couple of audit types to keep all of your wireless channel information in check.
Regulatory Logs: Keep detailed records of all regulatory filings, certifications, and correspondence. You never know when these will come in handy during litigation or if you need to double-check some advice.
Configuration Logs: Configuration Logs should document all changes to wireless devices, including frequency, power, and security settings.
Train Staff on Regulatory Requirements and Procedures
Make sure your organization develops role-specific training for your employees. With regard to wireless channels, professionals are either technical staff or compliance officers. Each group requires specific training to ensure adequate compliance and technical knowledge. Let's briefly go over each.
Technical Staff: Provide deep training for technical staff. Training should focus on installing and maintaining wireless technology.
Compliance Officers: Ensure compliance officers are well-versed in regulatory standards and auditing processes.
Audits keep tabs on the past, and training takes care of your future. Both of these practices are vital to your success as a wireless channel expert.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and maintaining compliance with wireless channels is essential in today's interconnected world. It's also an important concept to know for the Network+ Exam. Wireless channels facilitate communication through cell phones, Wi-Fi networks, and Bluetooth devices. These channels are vital to modern technology.
Mastery of their operation involves navigating complex regulatory landscapes. They are governed by organizations like the FCC, which ensures the safe and efficient allocation of frequencies. Following these rules helps organizations, making them more efficient and safe. Lastly, it preserves the reliability and integrity of wireless communications.
It's important to understand that technology is evolving. Staying informed and proactive in compliance is key to ensuring smooth operation and adaptation to rule changes.
To optimize your network's performance and analyze wireless channels, you can explore these wireless analyzer tools.
Want to learn more about network engineering? Consider taking the CBT Nuggets course Networking Fundamentals Online Training with Keith Barker.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.