What is Cisco BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection)?

Quick Definition: Cisco BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) is a network protocol that provides rapid fault detection by exchanging bidirectional hello packets between routers, ensuring quick identification of connectivity issues. It plays a vital role in enhancing network convergence by promptly notifying routing protocols to update routing tables when faults are detected.
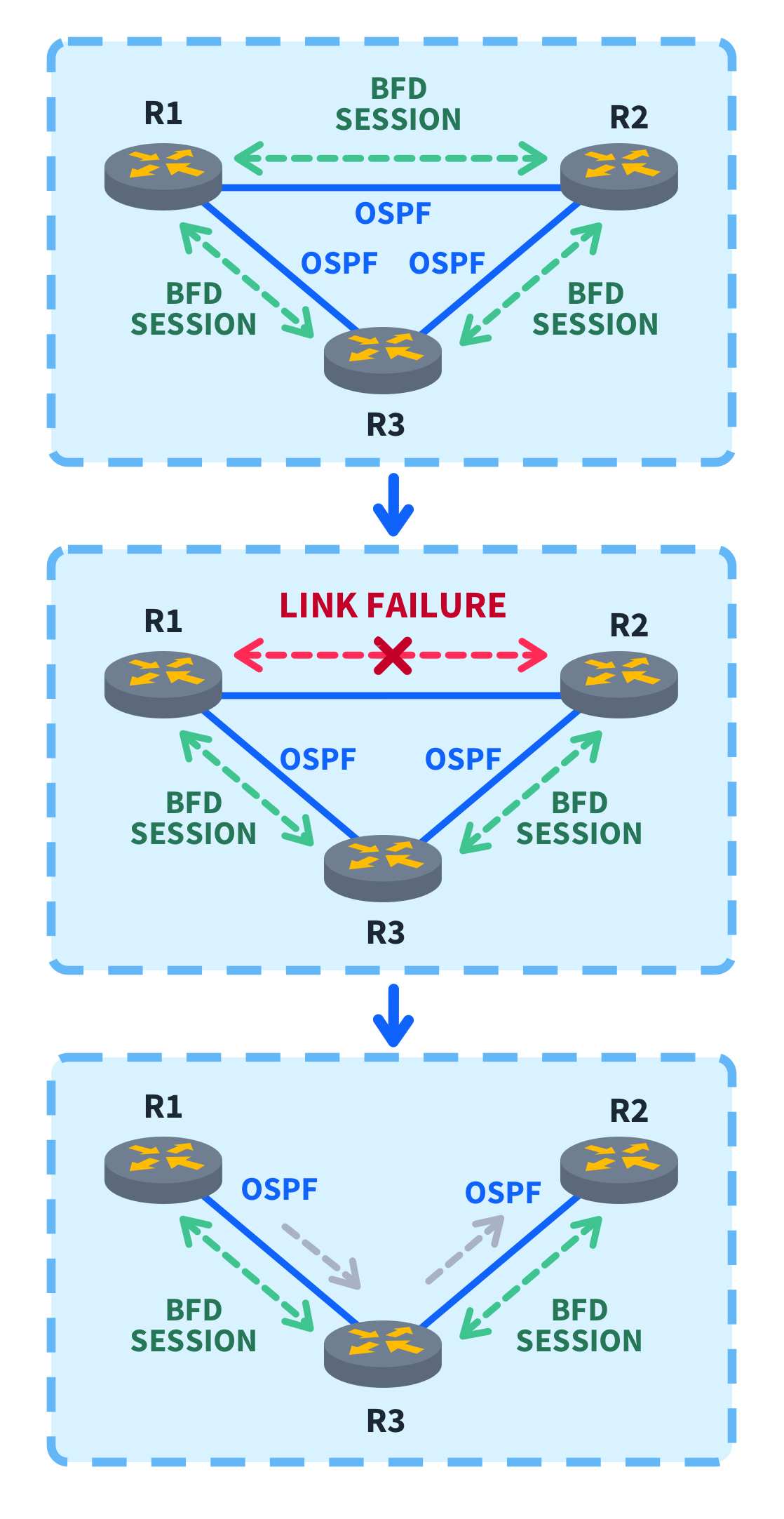
Cisco’s bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) is a mechanism that quickly finds faults and connectivity issues between two routers. BFD is protocol-independent, so it does not rely on the timeout time of any particular protocol and has its own method of detecting failure. It is remarkably efficient at detecting interruptions, taking just milliseconds to detect faults, and is a vital protocol for any Cisco network.
BFD is also a consistent topic on the Network+ Exam, making it crucial for those studying for the exam.
What is Cisco BFD?
BFD was first described in 2010 by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force.) As networks became more complex and sensitive to the need for rapid fault detection, it became crucial to have a dedicated protocol solely for router error detection.
Before the introduction of BFD, communication relied on protocol-specific dead times within protocols like OSPF or BGP. While these dead times could find faults within a second, the reality was that the detection and response times produced delays considered impractical for bandwidth-intensive operations like streaming and VoIP.
BFD also plays a crucial role in providing reliable convergence. In networking, convergence refers to the process where a router detects a fault and, with the assistance of BFD, rapidly identifies the next most optimum path. BFD notifies the routing protocols about the fault, and these protocols are responsible for updating the routing tables, ensuring the network adapts quickly to changes and maintains optimal communication paths.
So that’s the “what,” but it does not explain the how. Let’s go over how exactly BFD works and why it is called “bidirectional.”
How Does BFD Work?
BFD continuously monitors the liveliness of routers by sending low-overhead “hello” packets to each other. This continuous communication verifies that the routers are in an UP status. With that said, let’s break it down step by step to get a clearer picture of what is going on:
Session Establishment
A BFD session is established between two routers. These routers check up on each other to verify UP status.
Hello Packet Exchange
After connectivity has been established, the routers will begin exchanging the hello packets. These packets contain information on the health of the path. Packets are sent in a stream of millisecond intervals. Each router expects regular receipt of the packets.
Fault Detection
Here comes the good stuff. If a router fails to receive a hello packet in the specified time, it is considered a faulty path, and all routers are notified.
Notify the Routing Protocols
Next, BFD will notify the routing protocol used (Generally OSPF or EIGRP). These protocols will begin convergence since BFD does not explicitly handle that.
Convergence and Table Update
Once the protocols are notified, they recompute the optimal paths based on the changed network conditions. This involves updating routing tables to reflect the new topology and determining alternative paths for communication.
Stabilization
BFD begins forwarding hello packages based on the new routes. Once these are successfully sent and received, the network is considered healthy again.
To recap, BFD works by establishing a session between routers and constantly exchanging lightweight hello packets at a high frequency. Then, it continuously monitors the bidirectional liveliness of the forwarding path.
BFD’s ability to rapidly detect and notify network faults contributes to the overarching goal of fast and reliable network convergence.
How to Implement Cisco BFD
Cisco BFD configuration needs to be done on every participating router. First, make sure you have an accurate inventory of each router on your network. Since this is a Cisco proprietary protocol, the steps should be mostly the same.
However, there may be slight differences in your operating environment. With that said, let’s go over how Cisco BFD is typically implemented.
Enable BFD Globally
Enable BFD globally on all router interfaces. All router commands are in italics.
configure terminal bfd all-interfaces
Configure BFD on Specific Interfaces
Remember that routers have multiple interfaces, so we must configure which ones we want BFD to work with. GiganetEthernet0/0 is a typical router interface. To enable BFD on an interface, use the following command.
interface <interface_type> <interface_number> bfd interval <desired_interval> min_rx <minimum_receive_interval> multiplier <detection_multiplier>
Make sure this command is performed on every neighboring router!
Verify BFD Configuration
After configuring BFD on each router, use the following commands on each router to verify the status of BFD sessions:
show bfd neighbors show bfd neighbors details
These commands provide information about the BFD sessions, including the state, interface, and timers.
Final Thoughts
Cisco BFD may sound complicated at first, but it’s not as hard as it sounds. It is “bidirectional” because hello brackets are sent between routers. Like good friends, they are always checking up on each other. It is “forwarding” because the packets are always sent to a specific router destination. Lastly, it is “detection” because its explicit purpose is to detect faults and notify protocols to converge.
For successful implementation, Cisco BFD needs configuration on every participating router. Ensure a global specification and specify the interface where you want it to operate.
BFD works hand-in-glove with routing protocols like OSPF. It signals to OSPF to converge and update routing tables when a fault is detected. All of this and more can easily appear on the Network+ Exam, so ensure this critical concept is thoroughly understood.
Not a CBT Nuggets subscriber? Sign up and explore our Network+ courses.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.