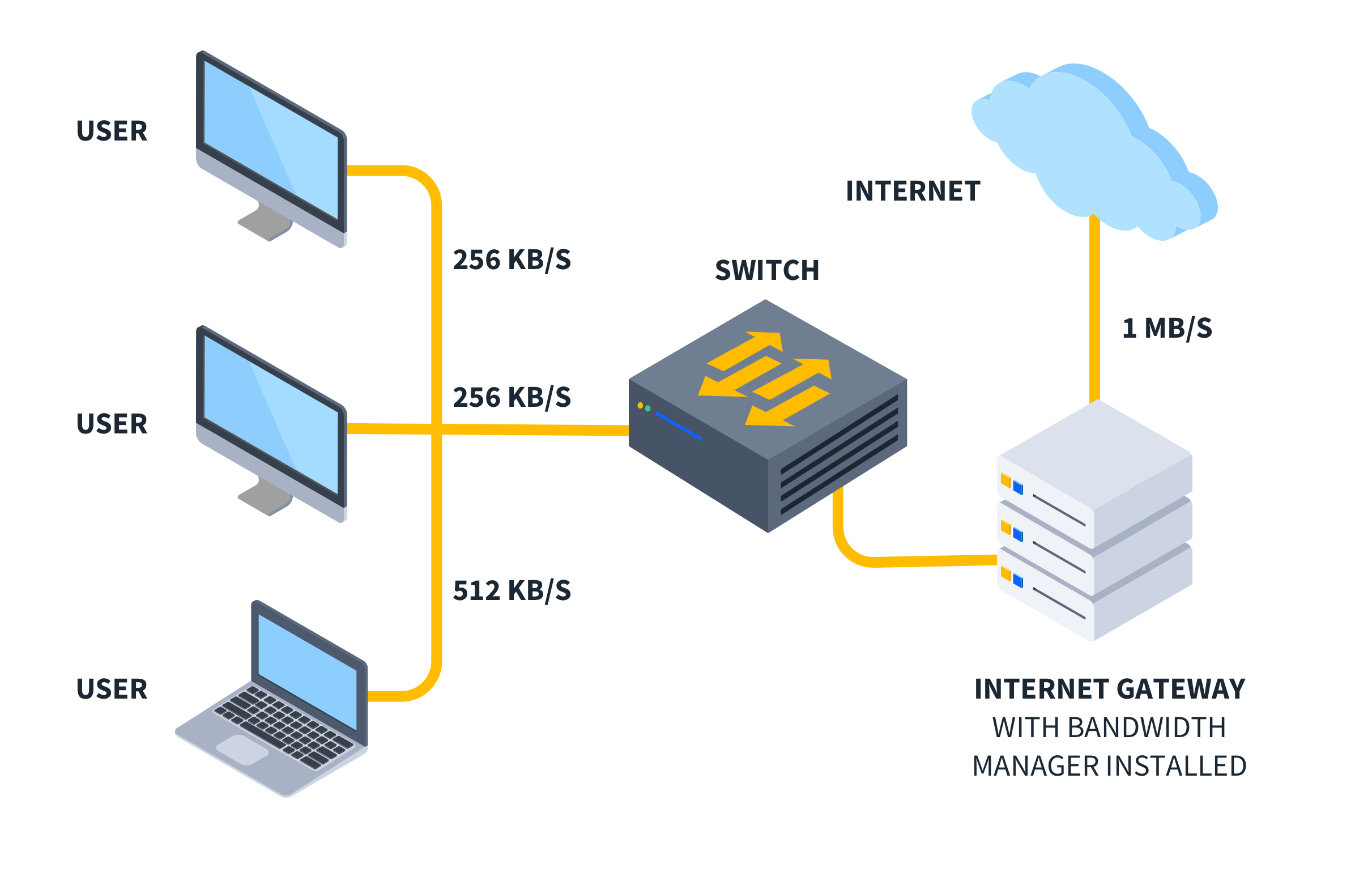
What is Bandwidth Management?

Quick Definition: Bandwidth management involves the strategic allocation and prioritization of data flow within a network environment to optimize performance and ensure efficient resource utilization. It encompasses techniques such as traffic prioritization, quality of service enforcement, and bandwidth allocation to maintain network stability, minimize latency, and meet the diverse needs of users and applications.
One of the most important aspects of running a business is proper resource management. In internet-reliant companies, that includes careful management of data flowing to and from the internet.
Proper bandwidth management ensures optimal performance by prioritizing critical data transmission, reducing network latency, enforcing Quality of Service (QoS) policies, and limiting (or banning) non-essential data.
In this article, we’ll cover bandwidth management strategies, challenges, and why bandwidth management is crucial to overall network success.
The Basics of Bandwidth
Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can flow between two nodes on a network. Generally, it’s measured in Kps (kilobytes per second), Mbps (megabytes per second), or Gbs (gigabytes per second.)
Think of bandwidth like a river. The wider the river, the more ships can sail abreast down the water. Bandwidth is absolutely crucial to a functioning network. It ensures critical data such as voice calls, emails, files, and more are transferred quickly and with minimal impediments.
Upstream vs. Downstream
There are two types of bandwidth: upstream and downstream. Upstream is data that flows from your PC into the internet, while downstream refers to how quickly your PC can retrieve data from the internet.
Some upstream activities include uploading files, sending emails, or streaming content from the user's device to servers or other devices on the network — like Twitch. Downstream, on the other hand, refers to how quickly a PC can download data, stream data, access web pages, and transfer files.
Factors Affecting Bandwidth
Several factors can affect your bandwidth, but one of the biggest factors is the network infrastructure. The switches, routers, and cables used will have a large impact on the bandwidth capacity.
Another factor to consider is your Internet Service Provider (ISP). ISPs leverage different types of connections, such as fiber optics, DSL, cable, and more. Each of these connections offers different bandwidth ranges, with fiber optics generally being the fastest.
Lastly, network administrators may enforce QoS policies that affect how quickly data is transferred on the network. They often allocate different resources for different users or services — we’ll discuss this more in-depth later.
Why is Bandwidth Management Important?
Effective bandwidth management is crucial to any organization that uses the internet. Let's delve into several reasons why it deserves careful prioritization.
Cost Efficiency
Effective bandwidth management can help organizations optimize their network usage, potentially reducing costs associated with unnecessary bandwidth usage or overprovisioning.
Performance Optimization
Proper bandwidth management ensures critical applications and services receive sufficient bandwidth. This prevents slowdowns and maintains optimal performance. Bandwidth management helps distribute network resources fairly among users and applications, preventing any single entity from monopolizing bandwidth to the detriment of others.
Prevent Network Latency and Downtime
By prioritizing critical data transmission, bandwidth management reduces latency, ensuring that information reaches its destination promptly. For example, VoIP data can be prioritized to provide optimal service to business calls, while a minimum amount of bandwidth is provided for emails and their attachments.
Enhance User Experience
Bandwidth management enhances user experience by ensuring important data has sufficient bandwidth. For example, software developers may be given extra bandwidth to download applications because their work is crucial to overall business success.
5 Strategies for Effective Bandwidth Management
Here are several strategies to help you prioritize data when and where your organization needs it most.
1. Prioritize Traffic
First, decide what network traffic is considered critical. It can be VoIP, emails, HTTP, or something else. For example, a 911 emergency service likely allocates as much bandwidth as possible to telephonic services. Or, a sales company could allocate bandwidth to VoIP calls so that deals are never interrupted. Determine which applications, services, or protocols are the lifeblood of your organization and implement QoS policies to help them thrive.
2. Implement Quality of Service
Quality of Service is a group of policies that ensure bandwidth is managed effectively. One of the most common QoS policies is class-based queuing, which divides network traffic into classes based on specific criteria, such as application type, source/destination IP address, or protocol.
Each class is then assigned a guaranteed minimum bandwidth allocation, allowing critical applications to receive preferential treatment while still ensuring fair sharing of available bandwidth among different traffic types.
3. Leverage Bandwidth Monitoring and Analysis Tools
There’s an old adage that says, “If you’re not measuring, you’re not managing.” That adage is truer than ever in bandwidth management. Numerous monitoring and analysis tools can help you determine which services hog the most bandwidth and what can be done about it.
Wireshark: Wireshark is an open-source packet analysis tool that captures and analyzes data packets in real-time. It allows network administrators to analyze network traffic, identify bandwidth usage patterns, and troubleshoot performance issues.
NetFlow Analyzer: NetFlow Analyzer is a network traffic analysis tool that collects and analyzes data from routers and switches. It provides insights into traffic patterns, application usage, and bandwidth consumption, helping administrators optimize network resources and troubleshoot performance issues.
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM): Last on the list is SolarWinds NPM. NPM is a great tool that offers in-depth bandwidth analyses for both upstream and downstream applications. It provides visibility into network traffic, application performance, and device health, allowing administrators to identify bandwidth bottlenecks and optimize network performance.
4. Bandwidth Allocation
As a network administrator, sometimes you have to do the unpopular thing and throttle bandwidth for users. Luckily, it makes everyone’s life better in the long run. By implementing bandwidth limits, organizations can ensure all users and applications receive a fair share of available bandwidth. This prevents any single user or application from monopolizing network resources and degrading the performance of others.
5. Use Traffic Shaping and Throttling
Traffic shaping and throttling are common QoS policies that ensure a robust network. Traffic shaping is a technique used to regulate the flow of network traffic by controlling the timing and volume of data packets transmitted across the network.
It smooths outbursts of traffic and enforces bandwidth usage policies by delaying or buffering packets to ensure they adhere to predefined traffic shaping rules. The goal of traffic shaping is to optimize bandwidth utilization, reduce network congestion, and improve the overall performance and reliability of the network.
Throttling, in contrast, involves intentionally restricting the amount of bandwidth accessible to particular applications, users, or devices to prevent them from excessively consuming network resources.
Throttling can be enacted temporarily or permanently on specific traffic streams, protocols, or IP addresses, either manually by network administrators or automatically according to predefined rules or thresholds.
The main purpose of throttling is to manage bandwidth utilization, reduce network latency, and ensure equitable distribution of resources among users and applications.
Best Practices for Effective Bandwidth Management
IT networks are ever-evolving environments, and network prioritization will change with the needs of the organization. With that in mind, here are several strategies to facilitate proactive bandwidth management.
Regular Network Audits and Assessments
Regularly assess your network from a bandwidth management perspective. Verify which applications take the most resources, which ones are used the most, and verify bandwidth is not allocated towards underused applications.
Verify your Ethernet cables are sufficient for the demands of the network and that routers are up-to-date on the latest firmware and software upgrades. By keeping your infrastructure up-to-date and analyzing application usage, you can make better use of your bandwidth and improve your end-user's quality of life.
Collaboration Between IT Teams and End Users
Unfortunately, network administrators do not have a crystal ball to discern exactly what the end-users need. Every so often, throttled applications may be more useful than IT realized.
This can eventually be discovered via packet analysis, but a quicker conclusion can be reached by having a conversation with some of the end-users. You can figure out what works and what doesn’t. This feedback loop is invaluable for ensuring bandwidth is managed effectively for the whole organization.
Regular Training and Awareness Programs
IT teams can educate end users about the importance of bandwidth management and provide guidance on how to optimize their usage to avoid overloading the network. This includes promoting best practices such as avoiding unnecessary downloads/uploads, scheduling bandwidth-intensive tasks during off-peak hours, and using bandwidth-heavy applications responsibly.
Bandwidth Management Challenges and Considerations
There are certain challenges and considerations that factor into bandwidth management. Here is a short list of considerations to keep in mind when developing a bandwidth strategy.
Balancing Performance Needs with Budget Constraints
It is important to think about the possible expenses that arise from bandwidth management.
Focus on optimizing bandwidth usage and network efficiency to make the most of available resources.
Implement traffic shaping, throttling, and quality of service (QoS) policies to prioritize critical traffic and manage bandwidth usage effectively. Monitor network performance and usage patterns continuously to identify opportunities for optimization and efficiency improvements.
Addressing Security Concerns in Bandwidth Management
While bandwidth management is a secure procedure, there are still some security considerations to keep in mind.
Traffic Encryption: Implement encryption protocols such as SSL/TLS to secure sensitive data transmitted over the network. Encrypted traffic may consume more bandwidth, so it's essential to balance security requirements with performance considerations.
Access Control: Enforce access control policies to restrict unauthorized access to network resources and sensitive data. Implement user authentication mechanisms, role-based access controls (RBAC), and network segmentation to limit access to authorized users and devices.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Deploy IDPS solutions to monitor network traffic for suspicious or malicious activity and prevent unauthorized access or data breaches. IDPS can help detect and mitigate security threats in real-time, protecting against network intrusions and attacks.
Final Thoughts
Effective bandwidth management is essential for organizations relying heavily on internet data transmission. By implementing bandwidth management strategies such as traffic prioritization, quality of service policies, and bandwidth allocation, organizations can optimize network performance while ensuring fair resource allocation.
Regular network audits, collaboration between IT teams and end users, and training programs are vital for proactive bandwidth management. However, it's crucial to balance performance needs with budget constraints and address security concerns to maintain a secure and efficient network environment.
Want to learn more about network engineering? Consider taking the CBT Nuggets course Networking Fundamentals Online Training with Keith Barker.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.