DWDM vs CWDM: When Should I Use CWDM?

Quick Definition: DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) and CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) are two multiplexing techniques used in fiber optics data transmission to enhance data flow. CWDM combines multiple wavelengths of light to carry data, making it suitable for shorter-range transmissions, like on college campuses, up to about 100 kilometers. Compared to DWDM, CWDM optimizes existing infrastructure and is a cost-effective, efficient way to increase data capacity without laying additional fiber optics, making it accessible to many users.
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) and Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) are common multiplexing techniques used in fiber optics data transmission. Both techniques greatly increase data flow by allowing multiple data channels to transmit simultaneously. However, in this article, we’ll hone in on CWDM.
Since CWDM is more commonly used, let’s start by explaining how it works.
What is CWDM?
Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) is a clever technique that optimizes light transmission to enhance data rates. It addresses the growing demand for fast internet access as more and more people seek to connect online. In the past, data would flow on a single wavelength, thus bottlenecking the data. CWDM, however, combines multiple light wavelengths, allowing data to travel on each one.
As a high-level analogy, think of CWDM as a multi-passenger van traveling on a highway. In traditional fiber optics, it's like a single-seater car driving down a street. The van in CWDM can transport several people (data) at once, each in their own seat. Now, in DWDM, those seats are closer together, allowing the van to carry even more passengers (data), increasing the highway's capacity.
Each wavelength that carries data is spaced 20 nanometers apart, which is farther apart than DWDM. This is why CWDM is considered “coarse” compared to DWDM. Generally, CWDM is used with single-mode fiber optic wiring. This is because single-mode fiber optics can travel significantly farther than multimode without the signal weakening.
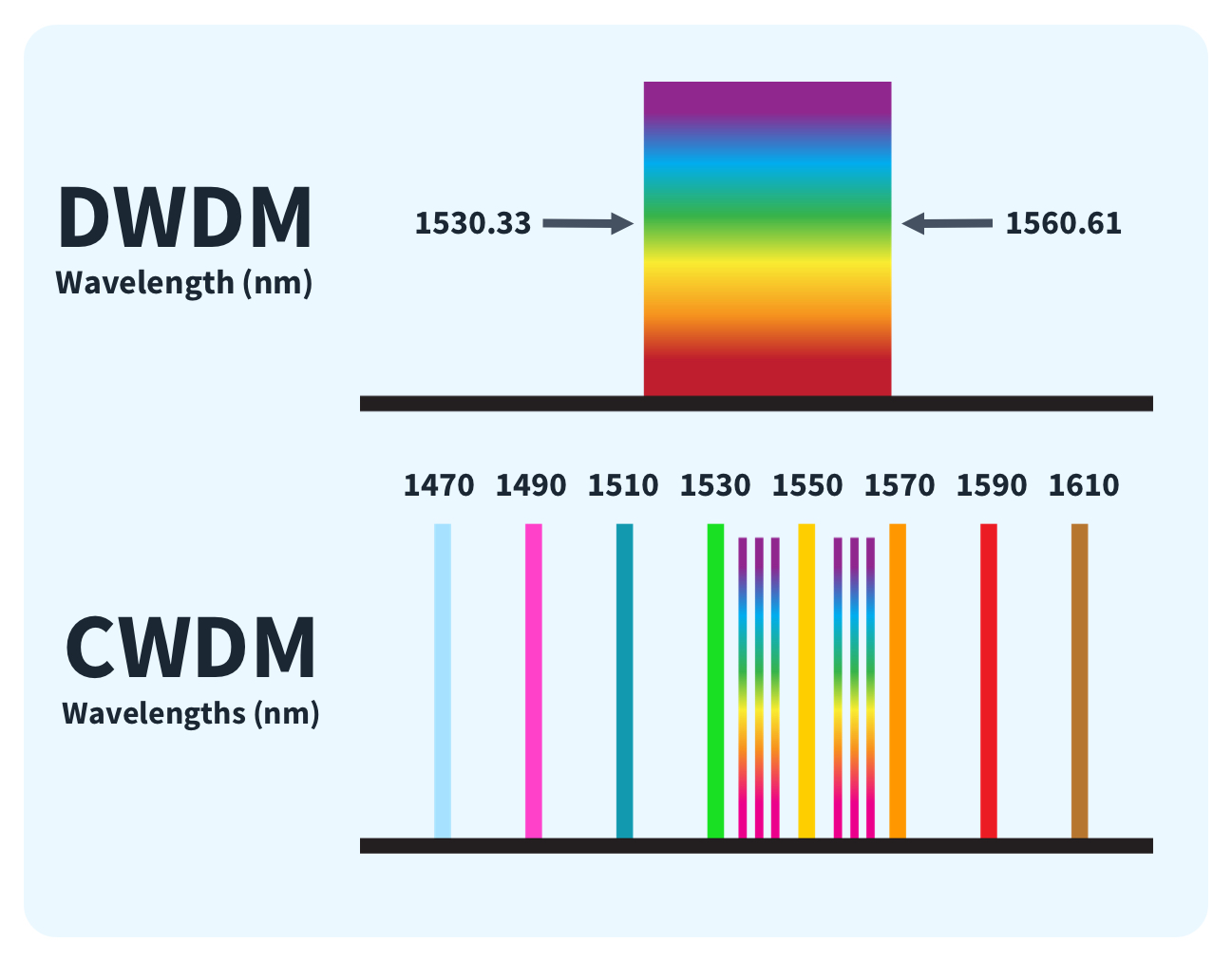
Due to its coarseness, CWDM is well-suited for shorter-range transmissions, such as on college campuses or metropolitan areas. In this case, “shorter transmission” means up to about 100 kilometers. Anything that requires a longer distance than that would benefit from DWDM.
How Does CWDM Work?
CWDM connects optical fiber cables into a multiplexer (MUX) that combines several data streams onto different wavelengths of light for transmission as a single cohesive flow. These distinct wavelengths represent specific data channels and are selected from a standard grid of wavelengths. Data streams can originate from various sources, including computers, printers, data centers, and more.
At the receiving end, a demultiplexer (DEMUX) divides the data back into its original streams, ensuring that each data stream reaches its intended destination. This process allows for efficient data transmission and sharing of the same optical fiber for multiple data streams.
We touched a little bit on DEMUX and MUX, but it takes more than a couple of multiplexers to make this magic happen. Let’s go over some of the additional equipment required.
What are the Components of CWDM?
CWDM (and LANs in general) requires various components and connections to work properly. Let’s list out all the required components needed when upgrading your fiber optics to CWDM.
CWDM Transceivers: These transceivers interact directly with devices on the network, such as routers, switches, and firewalls.
CWDM Multiplexers: This device combines different channels into one stream. This is the crux of CWDM.
CWDM Demultiplexer: This will perform the inverse operation of the MUX. This will take a stream of light and split them up.
Optical Fiber: Single-mode optical fiber is required to transmit the data. CWDM relies on the high travel capacity of single-mode fiber and its ability to send more data more reliably than multimode fiber.
Fiber Connectors: Appropriate fiber connectors, such as LC, SC, or MTP/MPO connectors, are used to connect the optical fiber to CWDM transceivers and other optical equipment.
CWDM Optical Attenuators: These are used to adjust the signal power of the light flowing through the CWDM system.
While this is not an all-inclusive list, this is the minimum required to get a network up and running with CWDM. Other equipment, such as a patch panel, will be required as the network grows in size and complexity.
What are the Benefits of CWDM?
There are several benefits of CWDM, including lower cost compared to DWDM, increased data capacity, installation simplicity, and more. CWDM is cost-effective because it reduces the need for additional fiber cable since more data can go through existing channels. For instance, if you have a room full of PCs, instead of having five lines run to the router, you can have one multiplexed line run up to the router, which splits into individual wavelengths of light.
CWDM greatly increases data capacity since data streams are multiplexed into just one stream. Since CDWM does not require the same level of precision as DWDM, it is easier to set up, test, and maintain.
What are the Applications of CWDM?
Due to CWDM’s excellent mid-range performance, it is often used on LANs, metropolitan areas, and college campuses. Not only is it optimal for these sorts of networks, but it is also a great resource for security and financial transactions.
For example, often, CWDM is used to send live video feeds from around the world to a central data center. In the same vein, CWDM is used by electrical grid operators to send valuable analytics to a central control room.
Lastly, CWDM can be used to interconnect data centers for redundancy purposes. Cloud computing relies on numerous data centers worldwide that can be quickly and reliably accessed. CWDM may be leveraged to acquire the high-speed, low-latency speeds that are the hallmark of cloud computing.
Final Thoughts
In the world of networking technology, Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) stands out as a cost-effective, efficient, and versatile solution. Its simplicity and ability to enhance data rates make it a valuable tool in the modern age of data transmission.
CWDM shines due to its low-cost implementation and ease of setup, making it accessible to many users. By optimizing the use of existing infrastructure, CWDM allows for increased data capacity without the need to lay additional fiber optics.
CWDM remains a practical and reliable solution as networking requirements continue to evolve, enabling networks to meet the demands of an ever-connected world. Its ability to deliver high-speed, low-latency connectivity makes it a key player in the pursuit of network speed and reliability.
Wiring the correct fiber optics for your organization is just a small piece of the networking puzzle. Here are a couple of other must-read articles to get you up to speed on building out a LAN.
Not a CBT Nuggets subscriber? Sign up for a 7-day free trial.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.