What is Port 88?
by Colin Cohen | Published on November 04, 2024
Port 88 is dedicated to the Kerberos authentication protocol, which allows clients to access privileged network resources by using tickets provided by a server.
To understand the purpose of port 88, you need to understand Kerberos.
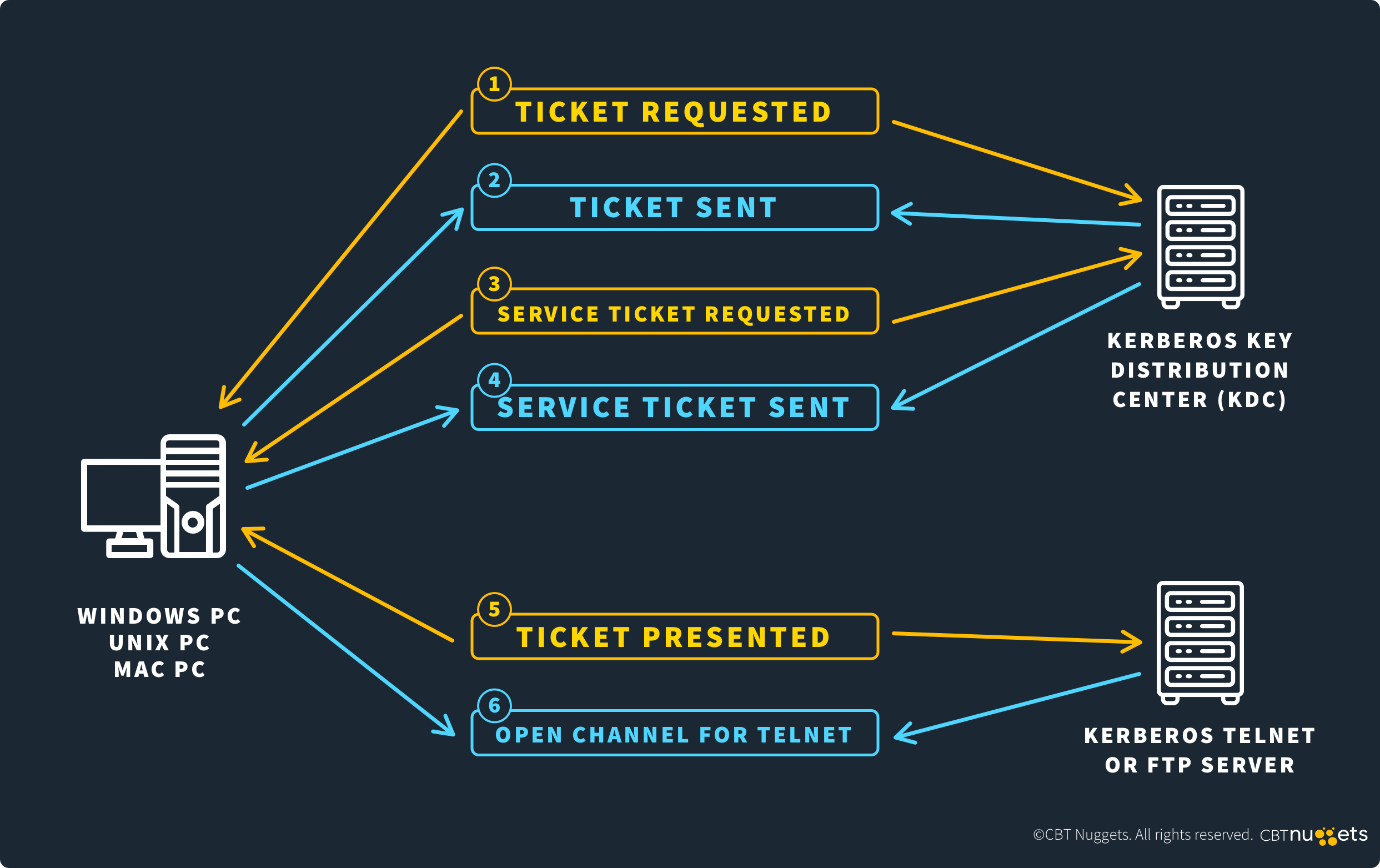
Kerberos is a common authentication protocol used by many applications, most notably Microsoft Active Directory (AD). It allows a client to access privileged network resources through tickets. A client requests a ticket from a server known as a Key Distribution Center (KDC). Once it authenticates the client, the KDC sends the client a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT), which the client can use to access various network resources without needing to reauthenticate for each one.
Kerberos clients communicate with KDCs over port 88.
Understanding Port 88
Port 88 allows clients to authenticate through the Kerberos protocol in applications such as AD and implements transport protocols underneath this protocol.
Technical Aspects
When a client wants to access privileged network resources, they authenticate themselves with a KDC over port 88 within the context of a client-server model. The KDC authenticates the client and sends them a TGT, which they can use to access multiple resources. Instead of authenticating for each resource, they send the TGT to the resource. TGTs expire over time but can be renewed prior to expiration, allowing users to have uninterrupted access to the network resources that they need.
The use of Kerberos over port 88 exists in the Application layer of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model.
Common Applications and Protocols
When using the Kerberos authentication protocol over port 88, you typically use User Datagram Protocol (UDP) as a transport protocol. This is because it is simpler and faster than the Transport Control Protocol (TCP). However, you need to enable TCP on the port as well to handle tickets larger than what UDP can handle.
The most common application that uses port 88 is Microsoft's AD.
How Port 88 Works
You use port 88 for Kerberos. The port allows users to authenticate themselves in enterprise networks with a limited impact on network performance.
Networking Basics
In a TCP/IP network, devices communicate with each other using IP addresses and ports. IP addresses identify devices on the network, and ports define the channels through which devices communicate. One such port is port 88.
Port 88 Specifics
Port 88 facilitates Kerberos. The port allows clients to authenticate themselves to KDC servers so they can access privileged network resources. Once a client has been authenticated, they can access a myriad of resources without having to authenticate to each one.
Port 88 in Different Environments
You will typically find the use of Kerberos and port 88 in enterprise environments. In these environments, users need to access many network resources simply and securely. Kerberos and port 88 allow them to authenticate a single time instead of for each resource.
Impact of Port 88 on Network Performance
The use of Kerberos on port 88 has a limited impact on network performance, especially in comparison with other authentication protocols. There is a small network overhead during authentication, but this is mitigated by the fact that users don’t have to authenticate for each resource.
Security Considerations
Using Kerberos over port 88 can lead to serious vulnerabilities. So, you need to implement best practices for securing the port on your devices.
Potential Vulnerabilities
There are a number of potential vulnerabilities associated with using Kerberos over port 88. These involve attackers getting access to user accounts with weak credentials and hacking KDCs to generate fake TGTs. In both cases, this can lead to serious information disclosure, so it’s important to properly secure port 88.
Best Practices for Port 88 Security
There are many ways to secure the running of Kerberos over port 88. They include:
Enforce the use of strong user credentials
Limit KDC access to known IP addresses
Keep Kerberos software up to date on your devices
Monitor network activity and investigate suspicious activity
Implement the strongest possible encryption
Troubleshooting Port 88 Issues
Implementing Kerberos over port 88 can lead to various technical issues. When problems arise, you need to know how to resolve them.
Common Problems
A number of common technical problems may arise when Kerberos is implemented over port 88. They include:
Date and time mismatches between clients and servers
Misconfiguration issues, including in firewalls
Excessive ticket sizes
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Process
When encountering an issue related to the use of Kerberos over port 88, the first step is to identify the problem. Given the wide range of potential issues that can arise when implementing Kerberos over port 88, covering each in detail is beyond the scope of this article; instead, we'll focus on some of the most common problems and general troubleshooting steps, which include:
Verify Date and Time Synchronization: Kerberos is sensitive to time discrepancies, so the first step is to ensure that the date and time on all clients and servers are synchronized. Even minor differences can cause authentication failures.
Check Network Connectivity: Confirm that port 88 is open on firewalls and that there are no network issues preventing communication between the client, the Key Distribution Center (KDC), and any intermediate devices.
Analyze Event Logs: Review logs on both client and server systems for Kerberos-specific error codes or messages. Most operating systems provide detailed Kerberos event logs that can help pinpoint where the failure occurred.
Validate DNS Configuration: Kerberos relies on DNS for hostname resolution. Ensure that DNS is correctly configured and that all Kerberos-related domain names are resolving as expected.
Inspect Kerberos Configuration Files: Misconfigurations in Kerberos configuration files (e.g., krb5.conf on Linux/Unix or registry settings on Windows) can lead to connectivity issues. Check for any incorrect or missing configuration details.
Test Ticket Requests: Use tools like klist on Windows or kinit on Unix/Linux to view or manually request Kerberos tickets. This can determine if ticket issuance or renewal is causing the problem.
FAQs
The following FAQs answer questions typically asked about port 88 and provide a basic understanding of the port and its uses.
What is Port 88 Used for?
You use port 88 for the Kerberos authentication protocol. This protocol allows clients to authenticate and then access multiple privileged network resources through tickets.
How Do I Check If Port 88 Is Open?
You can check if port 88 is open by running netstat -aon. You can run this command in a Windows command prompt or in a terminal when using Linux.
What Security Risks are Associated with Port 88?
Security risks associated with using Kerberos over port 88 relate to attackers gaining improper access to clients and servers. To protect your organization against these attacks, you should implement the guidelines described in Best Practices for Port 88 Security.
Can I Close Port 88 on My Network?
If you are not using Kerberos, you can close port 88 on the devices in your network. If you are using Kerberos, you should implement the guidelines described in Best Practices for Port 88 Security.
How Does Port 88 Relate to Kerberos?
Port 88 facilitates Kerberos. Clients authenticate with servers over the port. They then receive tickets from the servers that allow them access to privileged network resources.
Conclusion
You use port 88 when implementing the Kerberos authentication protocol. Clients communicate with KDC servers over the port so that users can effectively access privileged network resources.
As there are serious exploits associated with the use of port 88, it is important that you learn how to secure the port on your devices properly.