What is Port 593?
by Colin Cohen | Published on June 26, 2024
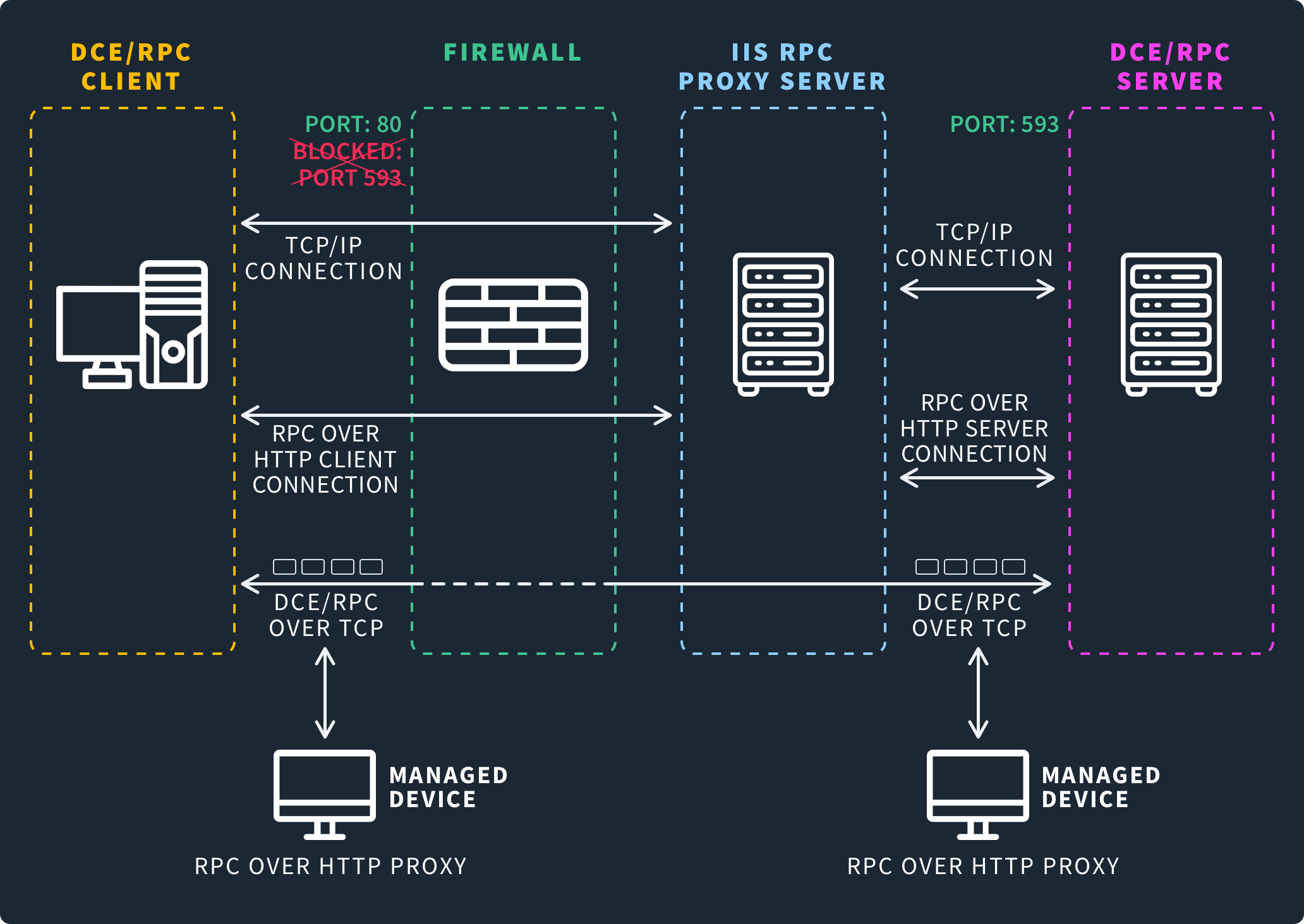
Port 593 is dedicated to the Windows Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Mapper Service. Unlike running the service on port 135, you do so over HTTP on port 593.
What is Port 593?
In Windows environments, port 593 is used when clients need to connect to servers remotely using the RPC Mapper Service. Running the service on port 593 instead of port 135 lets you run it over HTTP, which enables features that make the service more secure.
Definition and Significance of Port 593
Like with port 135, port 593 enables the RPC Mapper Service, which allows client devices to remotely connect to servers, to learn what services are running and on what ports they can connect to them. This enables many important Windows services, such as Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI). Unlike when running the RPC Mapper Service on port 135, on port 593 you run the service over HTTP.
Running the RPC Mapper Service on port 593 allows you to do so more securely, by adding the following features:
IIS Authentication: You can enable security mechanisms available in IIS, such as the disabling of anonymous access.
Traffic Encryption: You can encrypt traffic between clients and servers using SSL.
Device Limiting: You can restrict which devices can make RPC calls.
Protocol Association
You use port 593 to make remote procedure calls using the RPC protocol. The protocol lets you execute functions on a remote device over a network. You also make use of the HTTP protocol, as you run RPC on top of it. By tunneling RPC over HTTP, you enable features that make the RPC Mapper Service more secure than when running standard RPC over port 135.
Vulnerabilities and Security Concerns of Port 593
Despite its enhanced security features, the RPC Mapper Service over HTTP on port 593 is susceptible to a number of serious exploitations. So it is important to know how to properly secure it.
Common Vulnerabilities
If port 593 is left open on the public Internet, it can leave devices vulnerable to dangerous attacks, such as remote command executions (RCEs), sensitive data exposure, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Because of this, you must properly secure port 593 on your client and server devices that use the port.
Security Measures
If you are not working in a Windows environment or don’t need remote access and management, you probably should close port 593 on your devices.
Otherwise, you should restrict access to port 593 in your firewall to local IP addresses only. You should also consider implementing authentication and encryption mechanisms available when using the RPC Mapper Service over HTTP, such as IIS authentication, traffic encryption, and device limits.
Port 593 vs. Port 135
Port 593 and port 135 both enable the RPC Mapper Service, which is important for many Windows services. The difference is that, when you run it on port 593, you are making the service more secure.
The Differences Between Port 593 and Port 135
Both port 593 and port 135 enable the RPC Mapper Service, which lets remote clients connect to servers to learn what services are running on them and on what ports they can connect to them, something that is important for many Windows services. The difference between the two ports is that, when you use port 593, you are tunneling RPC over HTTP, making connections more secure.
Why Port 593 is More Secure than Port 135
When running the RPC Mapper Service, using port 593 is more secure than using port 135 because it adds additional security features, such as IIS authentication, traffic encryption, and device limiting. But this doesn’t mean that it is impervious to attacks. You still need to properly secure port 593.
Troubleshooting and Managing Port 593
If your organization uses the RPC Mapper Service over HTTP for remote access and management of your devices, you need to know whether port 593 is open on them and how to troubleshoot conflicts on the port.
Detecting Issues
To determine whether port 593 is open on a device, run the following command from a Windows command prompt:
netstat -aonResolving Common Issues
Only one service can listen to port 593 at a time. If you want to run the RPC Mapper Service over HTTP on port 593 and discover through the netstat command that another service is listening on this port, you will need to disable this other service before you can start the RPC Mapper Service over HTTP.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following FAQs answer questions typically asked relating to port 593. They provide a basic understanding of the port and its uses.
What is TCP port 593 used for?
You use TCP port 593 for the RPC Mapper Service over HTTP. This lets remote clients learn what services a server offers and how to connect to them. By running RPC over HTTP, it runs RPC in a more secure manner than when using RPC alone.
What is the vulnerability of port 593?
If you leave port 593 open on the public Internet, your devices can be susceptible to serious exploitations, such as RCEs and DDoS attacks. So, it’s important to implement security practices such as described in the Security Measures section.
Does the RPC Mapper Service Use Port 593 or Port 135?
The RPC Mapper Service can run over either port 593 or port 135. When you run it over port 593, you are doing so more securely, as it adds security features such as IIS authentication, traffic encryption and device limiting.
Is it Safe To Block Port 593?
If you don’t operate in a Windows environment or don’t need remote access and management over HTTP, it is safe to block port 593 on your devices. But if you do need it, you should leave the port open and instead implement security practices such as those described in the Security Measures section.
Conclusion
You use port 593 for implementing the RPC Mapper Service in a Windows environment over HTTP. It allows clients and servers to communicate for the purpose of remote access and management, and it does so more securely than when using the service over port 135. But as port 593 is still susceptible to a variety of serious exploitations, you must know how to properly secure the port.