What is Port 5353?
by Colin Cohen | Published on November 18, 2024
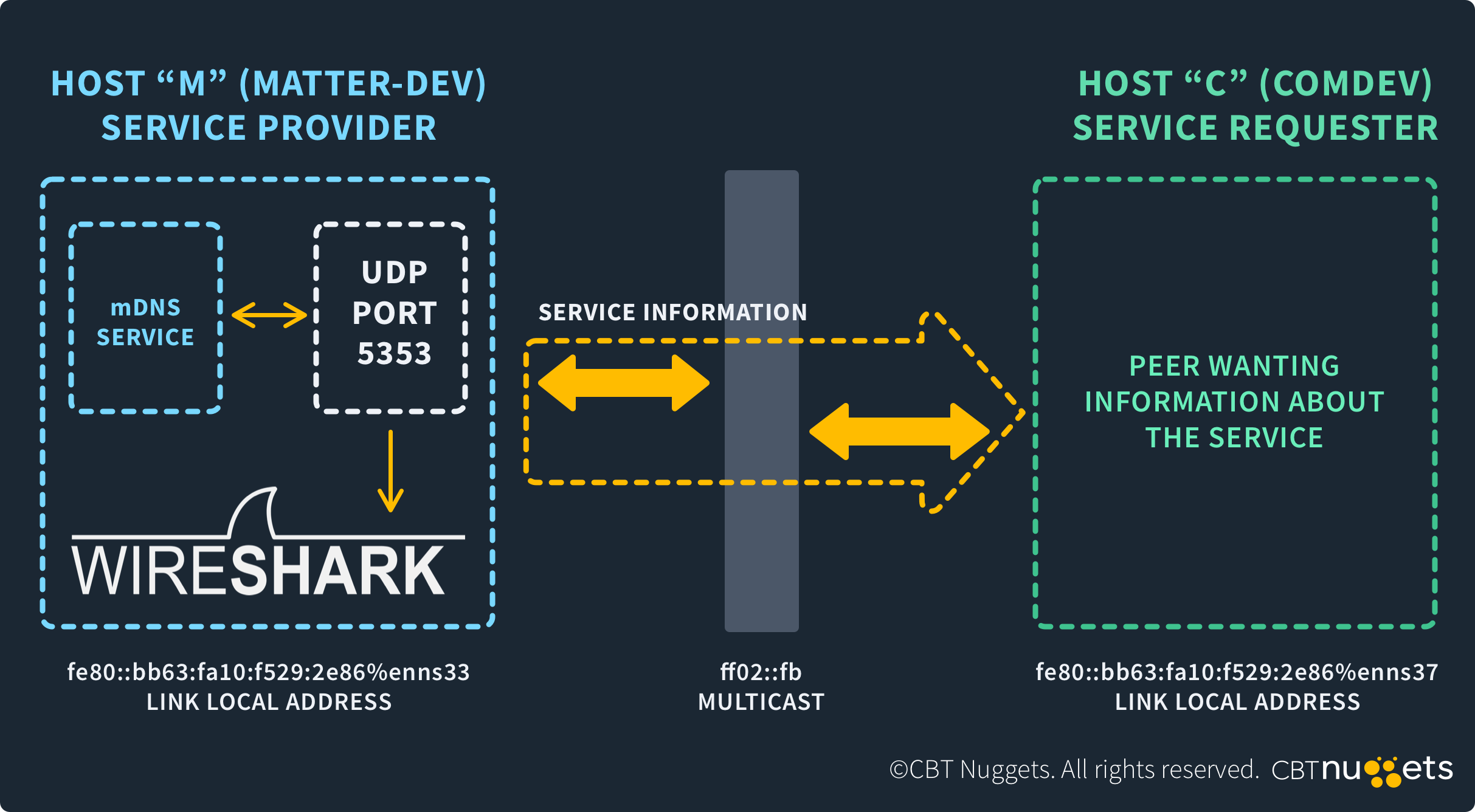
Port 5353 is dedicated to the Multicast Domain Name System (mDNS) protocol, which lets you resolve IP addresses in small networks without a DNS server.
To understand the purpose of port 5353, you need to understand mDNS.
In small networks, such as those in people’s homes, there is typically no DNS server to resolve hostnames into IP addresses. Instead, devices in these networks use mDNS. The protocol lets devices announce themselves to others in the network in a process called multicasting. This provides the devices with the IP addresses of others so that they can communicate with each other.
Understanding Port 5353
Port 5353 is for mDNS. It allows devices on small networks to announce their IP addresses so that other devices can communicate with them.
Definition and Technical Specifications
When using the mDNS protocol, devices on a small network announce themselves to other devices over port 5353. They broadcast their IP addresses using User Datagram Protocol (UDP) so that other devices can communicate with them, using a process called multicasting.
Common Uses
Small networks can contain many types of devices, such as computers, mobile devices, printers, and IoT devices. These devices use mDNS to communicate with each other. For example, if you add a printer to your network, the printer will announce its IP address through mDNS over port 5353 so that other devices can send files to print.
Multicast DNS (mDNS)
mDNS is a protocol that allows devices to multicast (announce) their IP addresses to other devices on a small network to facilitate communication between them. They do this over port 5353.
Role of Port 5353 in mDNS
Port 5353 enables mDNS. It allows devices on small networks to communicate their IP addresses to other devices over the port.
Real-World Applications
An example of a real-world application that uses mDNS is Apple Bonjour. This application lets devices on a small Apple-centric network discover other devices on the network and the services that they provide.
Security Aspects
Using mDNS over port 5353 can lead to serious vulnerabilities if the port is not correctly secured. Exploits can include distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and intrusions from devices outside the network.
Best Practices for Securing Port 5353
The best way to secure port 5353 on your devices is to prevent devices outside your network from accessing it. You can do this through your firewalls. You should also always keep your system software up to date.
Troubleshooting Port 5353
There are common technical issues relating to using mDNS over port 5353. You need to know how to resolve them and how to monitor traffic on the port. Common technical issues associated with using mDNS over port 5353 can include the following:
Excessive CPU usage on devices
Excessive network traffic
mDNS flooding
The best way to resolve these issues is to limit the use of mDNS to devices that actually require it.
Tools for Monitoring and Testing Port 5353
To test if port 5353 is open on a device, use the netstat -aon command in a command prompt or in a terminal.
To monitor activity on port 5353, you can use a port monitoring application, such as:
PRTG Network Monitor
Port 5353 in Different Operating Systems
All modern operating systems, including Windows, MacOS, and Linux, support the use of mDNS over port 5353.
Usage in Windows
Modern Windows operating systems support mDNS natively over port 5353. It requires no configuration to use it.
Implementation in MacOS
Apple-centric networks support mDNS over port 5353 through Bonjour. This product supports the discovery of devices and services on a small network, including those from other vendors.
Role in Linux Environments
Linux supports mDNS over port 5353 through Avahi. This product is similar to Apple Bonjour, in that it provides for the discovery of devices and services on a small network.
FAQs
The following FAQs answer questions typically asked about port 5353 and provide a basic understanding of the port and its uses.
What Is Port 5353 Commonly Used for?
Port 5353 is used for mDNS. The protocol lets devices on a small network multicast (broadcast) their IP addresses so that other devices on the network can communicate with them.
How Can I Secure Port 5353 on My Network?
The best way to secure port 5353 on devices in your network is to prevent devices from outside your network from accessing the port. You can do this through your firewalls.
Are There Any Known Vulnerabilities with Port 5353?
Vulnerabilities associated with using mDNS over port 5353 include DDoS attacks and network intrusions. Because of this, it is important to close off the port from the public Internet and only allow traffic from inside your network.
Why Does My Device Use Port 5353?
Your device uses port 5353 for mDNS. This protocol allows the device (and others on the network) to communicate its IP address to others on the network so that they can communicate with it.
How Do I Troubleshoot Connectivity Issues Related to Port 5353?
To troubleshoot connectivity issues relating to the use of mDNS over port 5353, follow the recommendations in the Troubleshooting Port 5353 section. It details common issues and how best to resolve them.
Conclusion
You use port 5353 for the mDNS protocol. This protocol allows devices on small networks to find each other’s IP addresses without a DNS server. However, the port has several serious vulnerabilities, so it is important to know how to secure it properly on your devices. Are you looking for a high-paying career in network administration? Earning a Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification can help you get there.