What is Data Loss Prevention?

Quick definition: Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a series of tools and processes designed to detect and prevent the loss, leakage, or misuse of sensitive data. It aims to prevent breaches, exfiltration, and unauthorized use.
Data security has become a serious concern for companies and organizations of all sizes. Cyber attacks are more common and have become more technically advanced in recent years.
Data has also become more valuable than ever, which makes protecting sensitive information very difficult—and more important than ever. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) practices and tools help IT personnel implement secure systems that don’t leak data. Together, we’ll find out more about what DLP is, how it works, and why it's so important for winning the battle against malicious forces that want access to your information.
What is Data Loss Prevention (DLP)?
Data Loss Prevention (DLP), is a holistic way to safeguard an organization's sensitive data from unauthorized access. It prevents both internal and external use and transmission of company protected data. DLP isn’t just a single solution; it is a range of different technologies, strategies, and processes designed specifically to identify, monitor, and protect data no matter what state it is in.
Data exists in different states, which are:
At rest
In motion
In use
Definition and Scope of DLP
DLP solutions have been designed to:
Identify sensitive data through inspection and contextual analysis. It can flag unauthorized applications being used to send data, and even block them outright if needed.
Monitor and control data movement across networks, endpoints, and cloud environments. If data transfers are detected, they can alert the user that they are sending data that is sensitive, and can cancel the transfer if it is a serious breach.
Enforce policies to prevent unauthorized data transfers. If an organization labels data as sensitive, DLP will help ensure the data is either inaccessible, or that it is not able to be shared or copied.
Provide visibility into data usage and potential risks, making management and security teams aware of what data is being accessed at all times.
Common Causes of Data Loss
Data loss in this context is not necessarily about losing data, like in a disaster scenario where Disaster Recovery (DR) is needed. Instead, data loss refers to data privacy being lost to unauthorized parties. Understanding the common causes of data loss is crucial for implementing effective DLP strategies:
Insider threats (accidental or intentional)
Phishing attacks and social engineering
Malware and ransomware infections
Lost or stolen devices
Misconfigured security settings
Third-party vendor breaches
Impact of Data Breaches
Data breaches can have serious consequences, including:
Financial losses due to fines, legal fees, and remediation costs
Reputational damage and loss of customer trust
Intellectual property theft
Compliance violations and regulatory penalties
Operational outages that affect business continuity
These potential impacts are no joke. DLP has become a necessary defense as part of a solid cybersecurity strategy for any business that handles sensitive data.
How to Incorporate DLP into Security Policies
To keep your data safe, DLP needs to be integrated into your organization's security policies. Period. No two businesses have the exact same requirements for DLP, which is something that doesn’t often get mentioned. That is why it is important to understand your DLP requirements before you start planning and implementing.
If your DLP policies are too strict, then some data might be flagged unnecessarily, while important data might not be protected well enough. To implement DLP that makes sense for your needs, you should:
Identify and classify sensitive data: Think about what data can’t be shared outside of certain departments, regions, or the company itself, and label it appropriately.
Assess risks and vulnerabilities: There is a fine balance between necessary security and needless inconvenience to your users.
Define clear objectives and scope for DLP initiatives: What are you trying to protect, and what are you willing to ignore? Defining this early on in your planning is important so you don’t lose sight of your security objectives.
Develop and enforce DLP policies across the organization: Your DLP needs to apply to all users and systems in a uniform implementation. This usually requires a DLP agent running on each system that has access to data.
Implement appropriate technologies and tools: You may find that both client side and appliance level filtering is needed when keeping track of a lot of data across multiple data channels. Find out if your needs are catered for in a single product, or if you need to apply a multi layered strategy to protect your sensitive data.
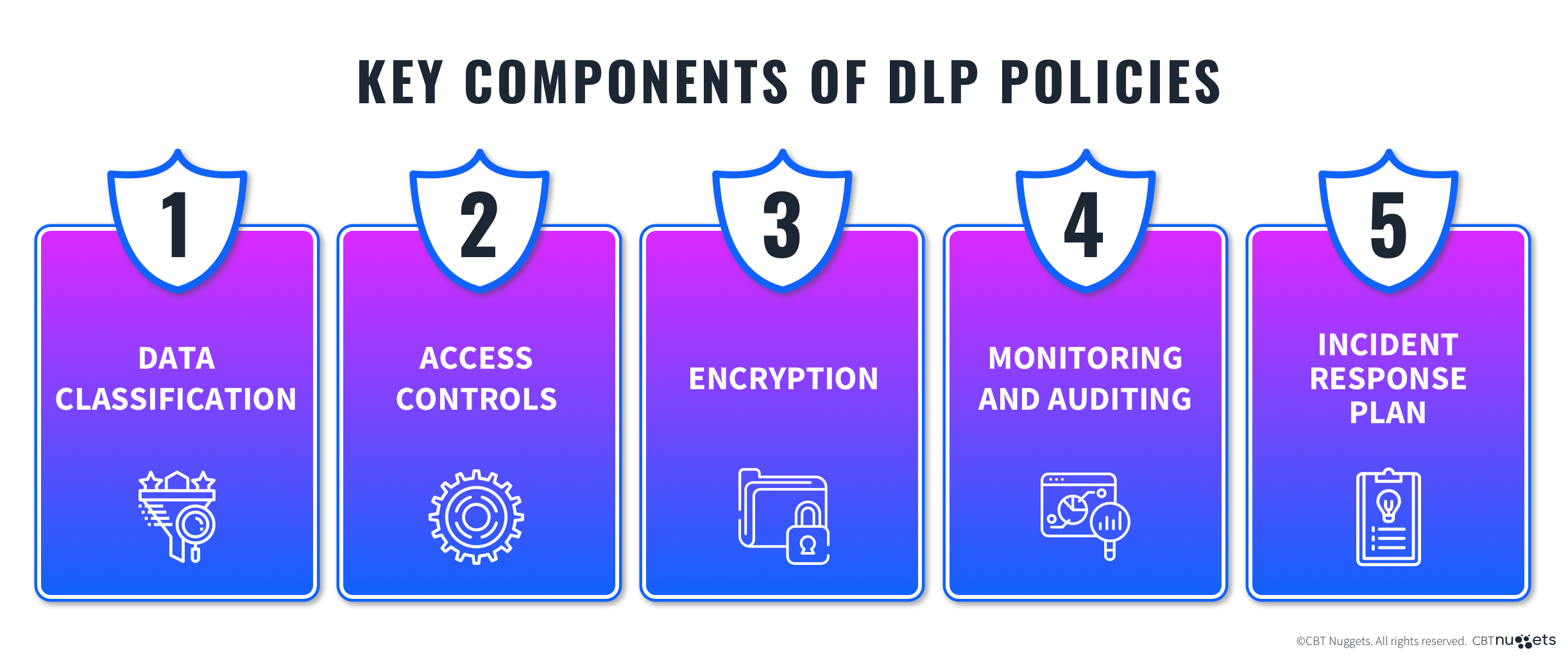
Key Components of DLP Policies
When you start planning your DLP policies, begin with a very basic plan. Below are some of the most simple concepts that you should include in your initial drafts when deciding on what DLP policies need to be rolled out.
1. Data Classification
Not all data is created equal. You need to categorize data based on how sensitive and important it is. That way you can prioritize the most critical data types and sources and make sure you protect it.
2. Access Controls
Not everyone needs to have access to all of your data within the organization. Most companies look to implement principles of least privilege and role-based access control (RBAC) to limit data access. It is easier to grant access to data via users and user groups than it is to manually assign data access per user.
3. Encryption
Whenever you transmit or store sensitive data, you need strong encryption. This applies to the data state classifications we mentioned earlier: data at rest, in transit, and in use.
4. Monitoring and Auditing
There is a lot of information associated with your data, and it needs to have eyes on it. You need to continuously monitor and log data movement and user activities so that you can analyze data usage for compliance and regulatory requirements. Some audits need this data to help you remain compliant.
5. Incident Response Plan
Incident Response is not just for cyber attacks. You need to develop and test your incident response plan to see how quickly it addresses and mitigates data breaches. You need to have teams available when a breach is detected so that you can understand what the breach is, and what it affects as fast as possible.
Regulatory Compliance and DLP
DLP helps you maintain important regulatory requirements. The most common ones are GDPR (personal data), HIPAA (health records), and PCI DSS (financial data). To maintain compliance, you'll need to show due diligence in the way you handle and protect sensitive data.
How to Implement Hardening Measures for DLP
Hardening your systems and networks can also help make your DLP strategy stronger. Here are some areas where this can be beneficial:
Securing Endpoints
Securing endpoints is crucial in protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access, as endpoint devices are often the most vulnerable entry points for cyberattacks. By implementing robust endpoint security measures, businesses can mitigate the risk of data breaches and ensure safer, more reliable operations.
Endpoint Protection Software: Software like antivirus, anti-malware, and DLP clients help lock down your endpoint devices, making your users less vulnerable, which hardens your of the most vulnerable points of data loss.
Device Encryption: When a personal device is lost or stolen, data is at risk—along with network access and other credentials. One of the best ways to minimize data risk to devices when this happens is to implement full-disk encryption.
Endpoint Configuration Management: Keeping your endpoint devices up to date is one of the most important ways that you can keep your data safe. Operating system and application vulnerabilities are discovered all the time, and they need to be patched as soon as a fix becomes available.
Network Security Measures
Your network is the gateway to your data, and it needs to be locked down as much as possible. Below are some of the most common approaches to take when it comes to securing your network.
Firewall Configuration: Firewalls are essential for maintaining your network's security. They decide what protocols are allowed in and out, and they need to set up in a way that maximizes their security without limiting your users to the point where it becomes counterproductive. There are many steps that can be taken to prevent unauthorized data transfers without impacting the functionality of your network.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): IDPS are able to detect and block potential threats and unusual activities, giving your teams visibility over the network as a whole. Alerts that are caught early and acted on can prevent serious damage to your network, and help to keep your data safe.
Network Segmentation: Much like a forest uses fire breaks to prevent the spread of wildfires, network segmentation isolates sensitive data and limits the potential impact of breaches when they happen. Complex network layouts make it more difficult for intruders to figure out where valuable targets are on your network and systems
Application Hardening
If your company creates its own software applications, there are many different approaches your developers can take into consideration when securing their existing and new products.
Secure Software Development Practices: Secure coding practices help to secure the access to data while it is being processed within the application. Regular security assessments should be carried out throughout the software development lifecycle, making sure that there are no common security flaws that allow prying eyes to inspect private data while it is in use.
Patch Management: Commercial products need to be tested constantly, and as security flaws and bugs become apparent they need to be patched. The same is true for products developed within your company, even internal applications that are only used within the organization.
Application Whitelisting: Application whitelisting is used to prevent unauthorized software from running, and helps to reduce the risk of malware infections by running suspect applications.
What are the Best Practices for Implementing DLP?
These are some best practices that can help you to maximize the effectiveness of your DLP:
Employee Training and Awareness
User education is important. You need to educate employees about data security risks and how they can prevent them. They need to be made aware of DLP policies and how they help to protect sensitive information. It's a continual process, making regular training sessions and awareness campaigns essential. When done right, user awareness can seriously reduce the risk of insider threats and accidental data leaks.
Regular Risk Assessments and Audits
Risk assessments need to be done often to help point out new vulnerabilities. Assessments help you to evaluate how effective your existing DLP measures actually are. When done regularly, audits can help you maintain compliance with both internal policies and external regulations- which is a win-win situation for everyone.
Collaboration with Other Departments
DLP can be daunting to implement, but remember that it isn’t only IT’s responsibility. Other departments need to get involved, from legal to HR—and departments all need to be involved to develop policies that cover as much important information as possible. Departments will have a much better idea of what data is important, so their input is really important to get it right.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
It gets said a lot, but security threats are always evolving. Your DLP strategy needs to be updated and refined to help meet new threats and methods, making it a never ending process. Continuously review and update your DLP policies and tools, along with your processes, so that you can recognize and deal with new threats and technologies as they appear.
Conclusion
Data loss prevention has become an important part of cybersecurity strategies. Implementing a solid DLP solution that integrates with your existing security policies can reduce your exposure to more threats. Combined with hardening measures, you can further reduce your risk of data breaches.
Remember that DLP is not a one-time solution. It’s a never ending process that needs to be continuously monitored and improved. The key to keeping your data safe is to continuously adapt. When you stay vigilant and keep your defenses up-to-date, your organization and its valuable data will be a much less desirable target.
Want to learn more about becoming a network security professional? Consider our CompTIA Network+ Training!
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.