What is VXLAN (Virtual eXtensible Local-Area Network)?

Virtual eXtensible Local-Area Network, also known as VXLAN, is a network virtualization technology that allows a single network to be used by multiple organizations without compromising security. With the increase of cloud technology, these data centers play a pivotal role in running key applications and businesses worldwide.
Understanding VXLAN is critical for IT professionals and network administrators because of the key role VXLAN plays in modern network architecture.
What is VXLAN? How Does it Work?
VXLAN is a tunneling protocol that is established between the source and destination network devices. It works by segmenting the Layer 2 ethernet frames and encapsulating them in UDP Packets (user datagram protocol).
This helps cater to the limitation of VLANs regarding virtual networks in cloud virtualization technology and provides a unique and scalable solution to the problem. VXLAN facilitates workload mobility and seamless migration by providing an abstraction layer that separates virtual networks from physical infrastructure.
Simply put, VXLAN allows a single network to be used by multiple applications or organizations. The organizations and businesses are like tenants in the network.
Just as tenants belong to a single building, with each apartment a separate entity, VXLAN is a discrete and private network segment within a shared network. Tenants cannot see the traffic from the other tenants or organizations, which improves network efficiency and enhances security.
How Does VXLAN Work?
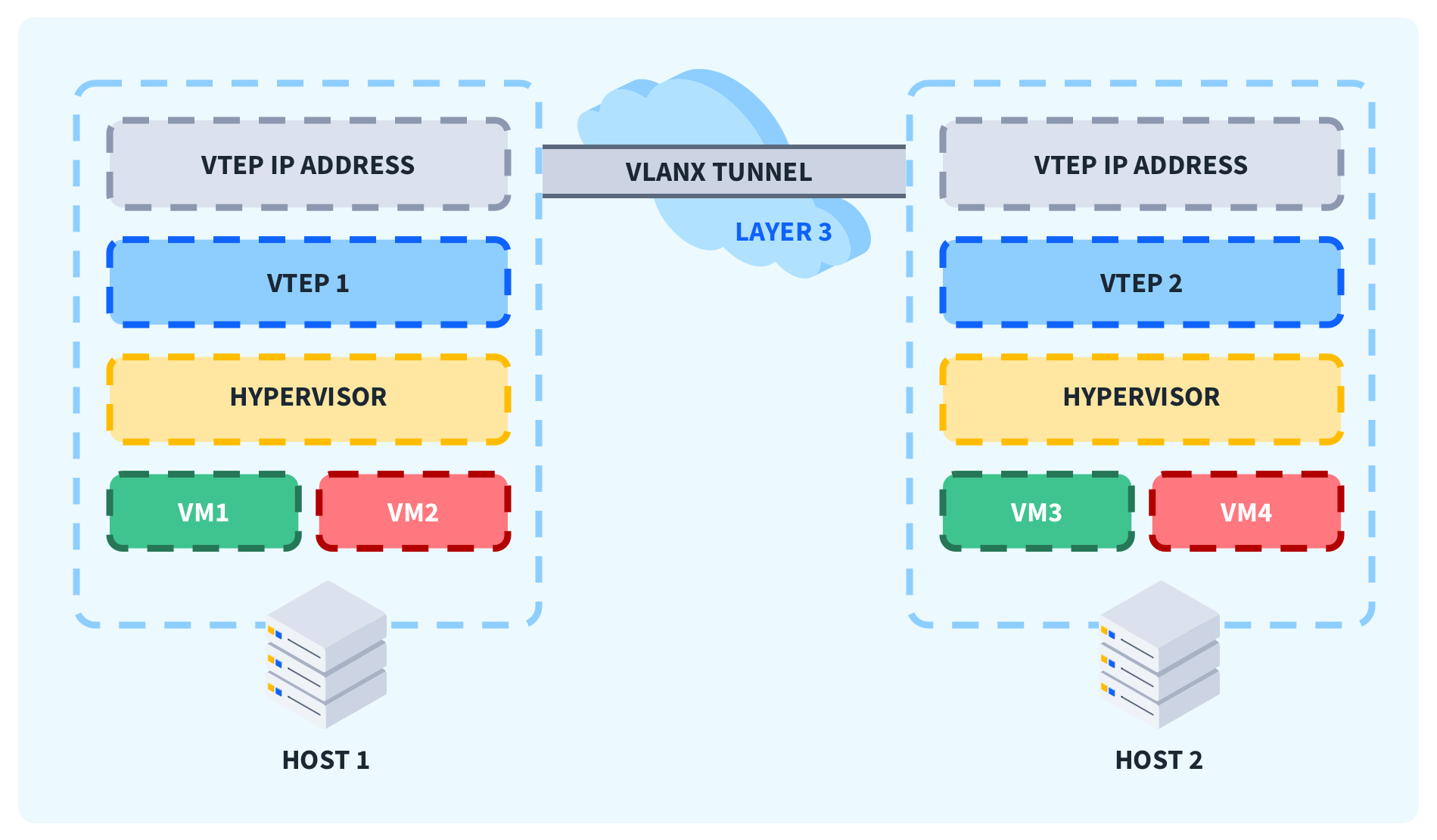
VXLAN operates within the Layer 2 data link layer by allowing segmentation of the layer and assigning a particular number known as VNI (VXLAN network identifier) to each virtual segmented network. The assignment of VNI helps isolate network traffic within Layer 2, by encapsulating ethernet frames into UDP packets (User Datagram Protocol). This enables traffic transportation over an IP network in the form of Layer 3 network infrastructure.
Virtual eXtensible Local-Area Network also creates overlay networks that allow for the creation of VXLAN networks, which are independent of any underlying physical networks. Network overlays play a very crucial role in modern networking and enable VXLAN to create virtual networks over existing physical infrastructure.
What are VTEPs?
VTEPs, which stands for VXLAN tunnel endpoints, are the devices used to encapsulate and decapsulation of VXLAN Network Packets. They could be physical switches and can also be virtual.
Through encapsulation and decapsulation of VXLAN segments, VTEPs ensure communication of virtual machines or devices of different VXLAN segments. For a better understanding of VXLAN, VTEP, and its applications in the modern world, explore CBT Nugget's Network + course for dedicated training material.
VLAN vs. VXLAN
VLANs help you create virtual networks within a LAN and group devices together that frequently communicate with each other. VXLAN is a network virtualization technology developed to overcome the limitations of VLAN by allowing a single network to be used by various organizations.
VLAN operates at Layer 2 and segments a physical network into multiple broadcast domains, while VXLAN operates at Layer 2 over Layer 3. Within Layer 2, it encapsulates ethernet frames into UDP Packets.
VLAN uses a 12-bit identifier, allowing 4094 networks over ethernet, while VXLAN uses a 24-bit identifier and can create up to 16 million networks. VLAN uses a spanning tree protocol, which blocks half the ports, while VXLAN allows all ports to be used, increasing efficiency. VXLAN is designed to be compatible with existing infrastructure and can coexist with traditional VLANs
Advantages and Limitations of VXLAN
VXLAN is useful in many situations due to its many advantages. Let's explore the benefits and limitations of this technology.
Advantages of VXLAN
VXLAN has a host of benefits, including:
Scalability: VXLANs are highly scalable, allowing up to 16 million isolated networks. This is very useful for organizations and data centers, allowing them to accommodate multiple tenants.
Dynamic VM migration: The movement of virtual machine hosts from one physical host to another without interruption of services or without letting the user know can be done through VXLAN. This is very important to maintain continuity of services and effective utilization of available resources.
Easily managed and configured: As VXLAN is a software network, it can be easily managed and configured with a centralized controller.
Privacy and security: Segmentation of networks allows for enhanced security and privacy so that one tenant is unable to see the traffic of the other tenant
Encryption: VXLAN inherently does not provide encryption, but encryption mechanisms can be employed with VXLAN.
Limitations of VXLAN
Despite the benefits of VXLAN, there are some limitations to be aware of. These include:
Additional cost: The encapsulation of Layer 2 within UDP packets can result in increased costs.
Complexity: VXLANs can become complex, especially when dealing with multiple segments and VTEPs.
Impact on performance when working with physical network devices: Enhanced MAC addresses and VXLAN traffic can impact the performance of physical switches and network devices.
How to Implement VXLAN
Implementation of VXLAN involves configuring VTEPs on network devices. VXLAN needs to be deployed on a downlink interface, through which access services are provided, and an uplink interface, which will be used to establish a VXLAN tunnel. Once VXLAN is deployed, packets can be forwarded to the network.
In short, VXLAN implementation can be summarized in three steps: packet identification, establishing a VXLAN tunnel, and packet forwarding.
Before implementing VXLAN, ensure the existing physical network is properly configured to support VXLAN. Enable VXLAN on interfaces and assign VXLAN a VNI to distinguish between virtual networks. After this, specify the UDP port. Then, configure VTEP IT addresses, specify remote IPs, and enable VXLAN on overlay interfaces.
Adjust configurations based on the network hardware about the specific device Setup can be verified through commands like ‘show vxlan tunnel’ and ‘show vxlan peers'.
Some deployments may use a network virtualization overlay controller (NVOC), which is to be used for automation and management of the configuration of VXLAN. Learn more about the VXLAN configuration and implementation.
Deployment of VXLAN
The method for deploying VXLAN is based on where the VTEP is located. Here are the three main ways to deploy VXLAN.
Host-Based VXLAN
With this method, deployment of VXLAN is done directly on individual host machines rather than on physical devices like switches. It is important to note that the host’s operating system must support VXLAN and relevant kernel modules or drivers.
Encapsulating and decapsulating is done through a virtual switch acting as a VTEP. Host-based VXLAN provides greater flexibility and control on the host level.
Gateway-Based VXLAN
Deployment of gateway-based VXLAN is done directly on network gateway devices like routers and Layer 3 switches. Encapsulating and decapsulating in a gateway-based VXLAN is done through a switch or router acting as a VTEP.
These devices are known as gateway VXLAN. This approach is commonly used to connect VXLAN-based virtual networks with non-VXLAN networks. Gateway-based VXLAN provides routing flexibility and interoperability.
Hybrid VXLAN
Hybrid VXLAN refers to deployment that combines gateway-based VXLAN and host-based VXLAN within the same network environment. Hybrid implementation is done with some VTEPs on hardware and some on virtual switches.
The hybrid approach incorporates the benefits of both VXLANs to provide flexibility, efficiency, and scalability.
Conclusion
VXLAN is an essential technology for data centers in a digitally growing world. It caters to the limitations of the VLAN, enhancing scalability, performance, security, and network virtualization through isolated segmentation in cloud environments.
Its ability to adapt to modern information technology infrastructures is unmatched, making it an important topic for all IT professionals, especially those studying for the Network + test.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.