What is Traffic Shaping?

Quick Definition: Traffic shaping is a technique used to control the flow of data packets, typically by delaying or prioritizing certain types of traffic. It is used to manage network congestion, optimize bandwidth usage, and improve overall network stability.
Efficient, dependable networks are the lifeblood of enterprises today, and the network administrator plays a key role. Their job includes making optimum use of available network resources so essential applications run well and with minimal service disruption. To achieve these goals, net admins need to fully understand concepts such as fault tolerance, quality of service (QoS), and traffic shaping.
When interviewing candidates for net admin positions, employers use certifications, such as CompTIA Network+ or Cisco’s CCNA, to gauge whether candidates have the required skills. Certifications ensure that job candidates have the core skills to implement and manage an enterprise network.
This includes setting up QoS and the policies to manage, prioritize, and control traffic as it traverses the network. Traffic shaping is one of the key techniques that net admins use to ensure that QoS is attained.
What is Traffic Shaping? Why is it Important?
Enterprises typically don't have a budget for unlimited network resources, so they need to make the most of available bandwidth. That's where traffic shaping comes in!
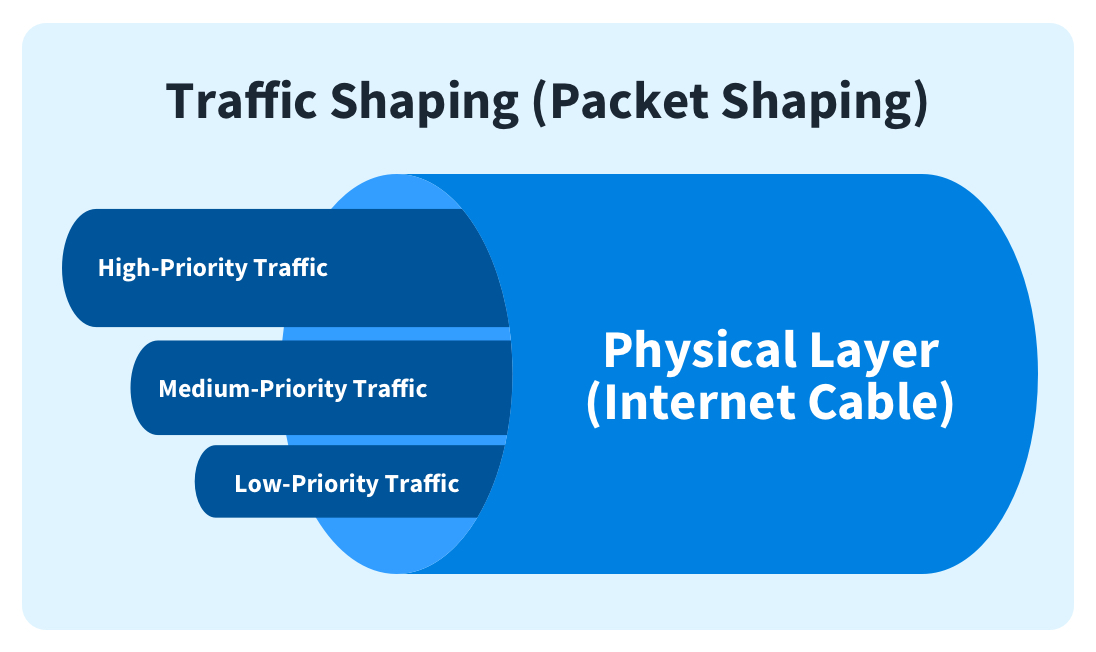
Traffic shaping is a quality of service technique for controlling the flow of packets. With traffic shaping, applications designated with high-priority QoS receive precedence over those from less important applications.
Depending on its traffic characteristics and importance to the enterprise, each application is categorized according to how its traffic should be handled. For example, a customer-facing web application may have a higher priority than an internal application.
Traffic for the external web application will be assigned additional bandwidth to meet its performance needs, while traffic for the internal app may be queued in buffers and thus delayed.
In another example, telephony (VoIP) or video conferencing may be categorized to receive priority assignment of bandwidth over lower QoS applications. Internet service or cloud providers may use traffic shaping to implement tiered subscription services, where customers pay increased fees to be assured of higher network speeds.
By using traffic shaping along with other bandwidth management techniques, organizations can ensure the performance of their high-priority applications. Traffic shaping also helps protect against external hacker attacks that try to overload the network.
Traffic from such distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks will be deprioritized compared to the traffic from designated high-priority systems. In this way, the effect of the DDoS attack is lessened.
What are the Benefits of Traffic Shaping?
A successful traffic shaping implementation helps minimize traffic congestion for high-priority applications, thereby boosting performance and stakeholder satisfaction. By helping make the best use of available network bandwidth, traffic shaping helps defer the need for expensive network capacity upgrades.
Traffic shaping also helps maintain the performance of priority applications in the face of external DDoS attacks. Overall, traffic shaping helps achieve quality of service (QoS) while meeting application performance targets and delivering expected return on investment.
What are Common Traffic Shaping Techniques?
Traffic shaping ensures the unimpeded flow of designated priority traffic by controlling – or limiting – the outbound flow of non-priority traffic. Traffic shaping can be application or route-based. When the networking equipment supports it, the application QoS can be determined at the protocol level from service bits in the IPv4 and IPv6 headers. In other cases, this determination must be made at a higher level from packet headers.
With application-based traffic shaping, the application is identified by a fingerprinting tool, and the packets are then processed according to the appropriate traffic shaping policy. If the application traffic is encrypted, then traffic shaping must be route-based – based on the source and destination addresses for the package stream.
In either case, when an application is identified as a high priority, the traffic shaping policy will drive the allocation of sufficient bandwidth and allow the unimpeded flow of packets.
Limiting the packet flow into the network is known as bandwidth-throttling, while outbound limiting is known as rate-limiting. Limiting is used for non-priority packet flows. Network admins control the amount of data by setting a bits-per-second controlled information rate (CIR). Non-priority traffic is diverted through buffers – and delayed – if it exceeds this rate on average.
Common Tools for Traffic Shaping
Traffic shaping is implemented at the command line level (CLI) of the networking infrastructure. For Linux traffic shaping, this is done by using the TC (traffic control) command. Network admins set up scripts that use TC commands to control how the network shapes and prioritizes traffic.
The TC command uses three constructs to implement Linux traffic shaping. They are queuing disciplines (Qdiscs), filters, and classes. Network packets leave the network via a Qdisc, which directs the path that the packet should follow. The filter is used to direct the packet into an appropriate class where the packet stream is shaped.
In Cisco environments, the net admin will use the Cisco iOS command line interface to configure QoS profiles, the related policies, and the Cisco traffic shaping rules.
What are the Best Practices for Traffic Shaping?
The first step in implementing traffic shaping is to ensure that the appropriate QoS categories have been established and that every application on the network has been assigned to an appropriate class.
Next, design the traffic shaping policies to support the QoS. Make sure that they cover low, medium, and high-priority application classes. Once implemented, the traffic shaping implementation needs to be monitored and adjusted as required.
Conclusion
Traffic shaping is an important technique every network administrator must master – whether for generic Linux traffic shaping or in vendor-specific situations, such as for Cisco traffic shaping.
If you're looking for a position as a network administrator, you can learn about traffic shaping and more by taking CBT Nuggets online certification training such as CompTIA Network+ (N10-009) or Cisco CCNA - 200-301, or Palo Alto Networks PCNSA.
Not a CBT Nuggets subscriber? Sign up and start studying today.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.