What is Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP)?

Quick Definition: Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is a vital IPv6 protocol used to manage communication between devices on a local network. It replaces and improves some IPv4 protocols and handles tasks like address resolution, router discovery, and network parameter configuration.
Modern networks are complicated beasts. If you want to tame them, then understanding protocols is something that you’ll have to grab with both hands. One of the protocols that roams within modern IPv6 networks is the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP). This article will explore NDP, its functions, and its significance in network operations.
What is the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP)?
Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is an essential part of the IPv6 protocol suite. It was designed to manage communication between devices on a local network. It is both a replacement and significant enhancement to several IPv4 protocols, including Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), ICMP Router Discovery, and ICMP Redirect.
But first, a little history. NDP evolved from ARP, an improvement that helped address limitations in IPv4 networks. NDP introduced new features to support the new and improved addressing capabilities of IPv6. While ARP was primarily responsible for handling address resolution in IPv4, NDP takes on more responsibilities in IPv6 networks.
The NDP protocol has quite a few components that it brings to the table:
Router Discovery: This allows hosts to find routers on the local network.
Address Resolution: IPv6 addresses are mapped to MAC addresses in a similar way that ARP does in IPv4.
Neighbor Unreachability Detection: Finds out if a neighbor is still reachable or not.
Duplicate Address Detection: This feature ensures that IPv6 addresses on the local link are unique and don’t conflict with other addresses.
NDP also offers features and functions that streamline network operations:
Stateless address autoconfiguration: Enables devices to configure their own IPv6 addresses without manual intervention or DHCP servers.
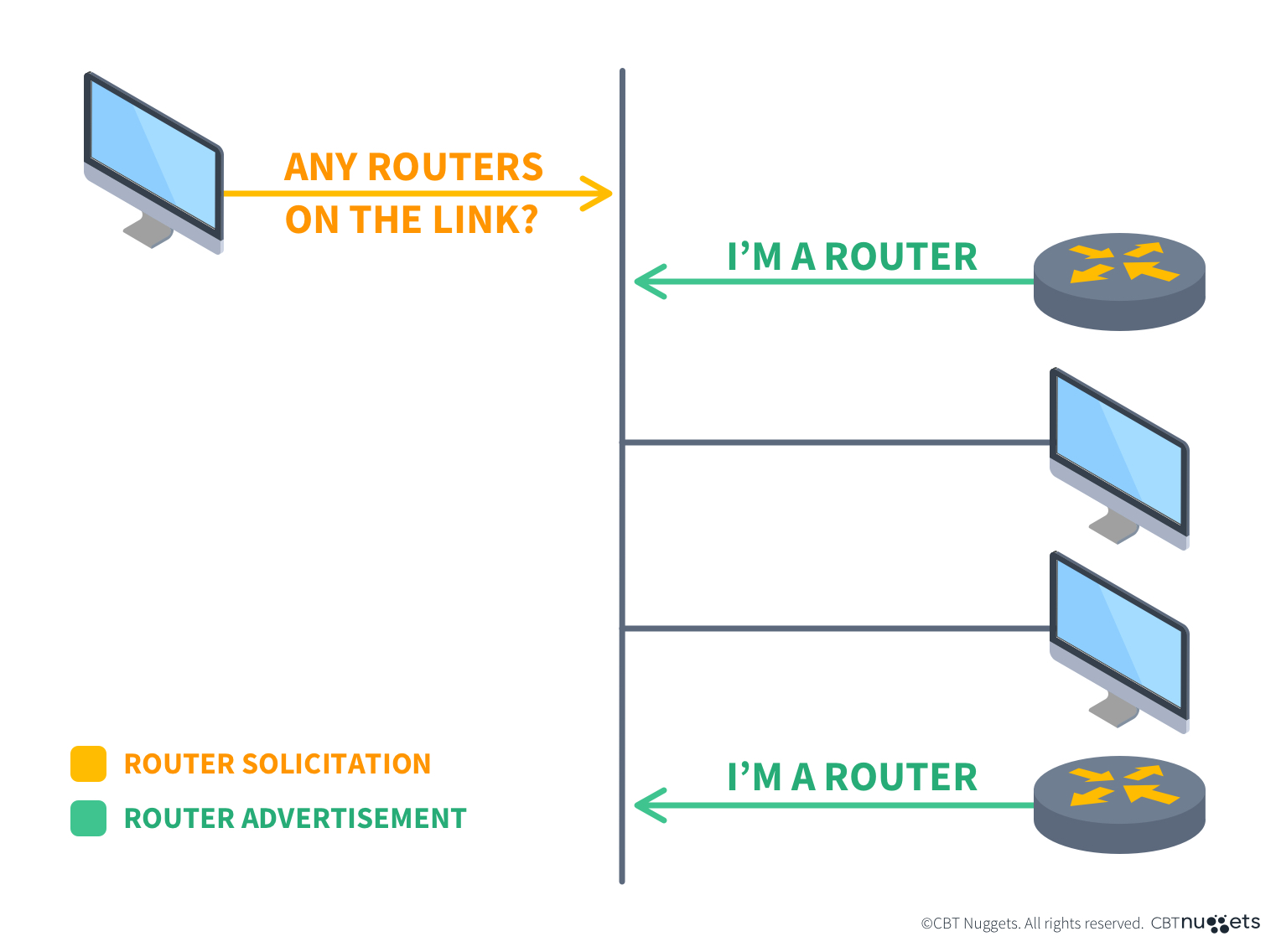
Router solicitation and advertisement: Allows hosts to request router information and routers to advertise their presence and network parameters.
Neighbor solicitation and advertisement: Facilitates address resolution and reachability confirmation between nodes.
While NDP brings plenty of benefits, it does have some vulnerabilities. The protocol can be vulnerable to NDP spoofing or Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. This is why we need to use available security measures like Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND) or RA Guard, which can help keep these risks from being exploited.
How Neighbor Discovery Protocol is Used in IPv6 Networks
Now that we know that Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) plays a central role in IPv6 networks, we can compare it to similar capabilities in IPv4.
Neighbor Discovery Protocol in IPv4 vs IPv6
In IPv4, a few protocols are needed to perform important functions on the network. The first is called Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). ARP manages IP-to-MAC address mapping and allows data to find its way to the correct devices on the network.
Next, there’s ICMP Router Discovery, which handles router discovery so that devices know where to send data that is destined for other networks. Lastly, we have ICMP Redirect, which manages path redirections when the original path is not accessible and needs to find another route. NDP in IPv6 combines these functions and provides a more streamlined solution.
How Neighbor Discovery Protocol Works in IPv6 Networks
In IPv6 networks, NDP performs a lot of functions all on its own. Below are some of the most important things that NDP does for IPV6 networks.
Address resolution: NDP maps IPv6 addresses to MAC addresses, similar to how ARP works in IPv4.
Router discovery: Like ICMP Router Discovery, NDP uses router discovery to allow devices to locate routers on the network.
Prefix discovery: This feature helps devices find which parts of the network they have direct communication with, also called on-link determination.
Parameter discovery: This gives devices all the parameters and settings that they need to work properly on the network.
Address autoconfiguration: Much like the name suggests, this helps with automatic IP address configurations for devices on the network.
Next-hop determination: When traffic is leaving the network, this helps with information about the next-hop details so that data is routed correctly.
Neighbor unreachability detection: This tells devices which destinations on the local network are available and tells them if a device is not available anymore.
Duplicate address detection: This prevents duplicate addresses from causing conflicts on the network.
Advantages of Neighbor Discovery Protocol in IPv6 Environments
Some of the advantages that NDP offers in IPv6 networks are:
Simplified Network Configuration
When it comes to network configuration, simple is best. Stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC) allows devices to configure their own IPv6 addresses without manual configuration or DHCP servers.
Automatic router discovery lets us say goodbye to setting manual default gateway configurations; it's all done automatically.
Improved Security
IPv6 has IPsec by default, which can be used to protect NDP messages and ensure their authenticity.
The Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND) protocol adds another layer of security, with proof of address ownership and message protection.
Better Network Efficiency
Multicast-based neighbor discovery increases network efficiency by reducing network traffic compared with IPv4's broadcast-based ARP.
Neighbor Unreachability Detection optimizes data transmissions by quickly identifying unreachable nodes and using other routes when necessary.
Packet size is optimized with Path MTU discovery, which also increases network efficiency.
With all of these improvements, we can build IPv6 networks that are stronger, safer, and more efficient than older IPv4 networks. To take advantage of all of these new features, we have to understand how NDP (Neighbor Discovery Protocol) works in IPv6, especially now that more organizations are making the switch.
What are Some Real-World Applications of NDP?
Now that we know what Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) does in network environments, we can look at some of its real-world applications. Below are some examples of what NDP does in different scenarios.
Neighbor Discovery Protocol in Local Area Networks (LANs)
In LANs, NDP is responsible for smooth communication between devices on the same network segment. Here are some of the nifty things it does for us on a LAN:
NDP handles the automatic IP address configuration for devices joining the network, which is less disruptive than how ARP handles addressing in IPv4 networks, which broadcasts requests to every host on the LAN.
It allows devices to discover routers on the local network. When a host joins the network, it sends a Router Solicitation message (RS) to find out what routers are available. The router responds with a Router Advertisement (RA), which contains important information about itself, such as its IP address, network prefixes, and other configuration details.
NDP offers a quick resolution of IPv6 addresses to MAC addresses for local communication. When a device wants to talk to another device on the same subnet, it sends a Neighbor Solicitation (NS) message. This is a request for the MAC address that is associated with a specific IPv6 address. The target device then responds with a Neighbor Advertisement (NA) that has the requested MAC address information that was requested.
NDP also prevents duplicate IP addresses on the network by using something called Duplicate Address Detection (DAD).
When we add all of these features together, we get self-configuring, efficient local networks that don’t require much manual setup from us, which is always welcome!
Neighbor Discovery Protocol in Wide Area Networks (WANs)
When we think of NDP, we normally associate it primarily with local links, but it also plays a role in WANs.
NDP helps with the discovery of first-hop routers for communication across network boundaries, which allows traffic to find its way to other network segments.
It also handles address resolution for devices on different network segments. Once the MAC address has been received, the device sends traffic to other segments via the router. The router then ensures correct routing between segments, which is seamless.
IPv6 mobility is possible because NDP allows mobile nodes to discover new routers when they move between networks.
What are Common NDP Issues and Troubleshooting Methods?
In most cases, NDP works flawlessly. But as with all things related to tech, it has its moments. You might come across occasional issues that can cause problems on the network, so understanding what they are and how to fix them is really important if you are supporting a network with IPv6 running NDP. We’ve gathered some common issues and troubleshooting steps that will get you started.
Address Resolution Failures
Address resolution is one of the main NDP functions responsible for mapping IPv6 addresses to MAC addresses. If you are having problems with address resolution, then you could have some of these symptoms:
Incomplete neighbor cache entries: The neighbor cache stores mappings between IPv6 addresses and MAC addresses. If you have incomplete entries, it can lead to communication problems and IP address conflicts.
Firewall rules blocking NDP messages: Firewalls can block essential NDP messages (like Neighbor Solicitation and Neighbor Advertisement that we mentioned earlier), which will also disrupt address resolution.
Network congestion causing packet loss: If you have high packet loss, it could be due to network congestion. Congestion can affect NDP messages and address resolution.
Basic Troubleshooting Steps:
Use the "ping" command to test connectivity to target devices on the network and check the consistency of the replies.
Check the Neighbor Cache with "ip -6 neighbor show" and look for inconsistencies in the mappings.
Verify that your firewall rules aren't blocking ICMPv6 messages.
In some cases, you’ll need to analyze network traffic with tools like Wireshark to figure out if you are losing NDP packets.
Neighbor Unreachability Detection Issues
Neighbor Unreachability Detection (NUD) makes sure that nodes can communicate with their neighbors. Problems are usually caused by some of these issues:
Nodes fail to respond to Neighbor Solicitation (NS) messages, which will disrupt communications on the network.
Asymmetric routing causes reachability conflicts because incoming and outgoing routes are different.
Misconfigured timers can potentially lead to premature neighbor entry expiration.
Basic Troubleshooting Steps:
Use "ping" to test bidirectional connectivity. Check if you are getting responses, and if possible, try using the ping command from the target device.
Check your router’s configuration for asymmetric routing.
Sometimes, it is necessary to adjust NUD timers if you are having reachability issues.
In some cases, you’ll need to analyze network traffic with tools like Wireshark to monitor NDP packets.
Duplicate Address Detection Problems
Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) prevents IP address conflicts, but issues can happen when these problems occur on the network:
Misconfigured nodes repeatedly attempting to use the same address can cause conflicts.
Network delays causing false positives in DAD lead to address conflicts.
Malicious nodes responding to all DAD requests will cause disruptions.
Basic Troubleshooting Steps:
A good place to start is to check the system logs for DAD failures. This will help you pinpoint where the issue is coming from and whether the problem is still active.
You can use "ip -6 address show" to look at the current address states on suspect devices.
In some cases, you might need to analyze network traffic with WireShark or other packet inspection tools to detect suspicious DAD responses.
Implement Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND) to prevent DAD attacks.
Best Practices for Resolving NDP-Related Issues
Prevention is better than cure, but sometimes, you will still need to troubleshoot NDP problems. Either way, these best practices can help you stop issues from appearing on your network and troubleshoot them more effectively when they do happen.
Use Monitoring Tools
Using network monitoring software to track NDP performance will let you detect issues early, buying you precious time when things go wrong. Also, look at setting up alerts so that you can pick up any abnormal NDP behavior or unusual traffic as it happens.
Regularly Update and Patch
Basic housekeeping can go a long way. By simply keeping all of your network devices and operating systems up-to-date, you can get the latest features and fixes as they become available. For known issues, you’ll need to apply security patches as soon as possible to plug any vulnerabilities present on your network.
Optimize NDP Parameters
If you are having conflicts or other connectivity issues, you should adjust your NDP timers based on your network size and layout. Also, consider configuring queue sizes for NDP message processing and other parameters to fine-tune your network until you are happy with its performance and reliability.
Security Measures
Basic security measures like Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND) can protect against NDP-based attacks, and configuring RA Guard on switches can also prevent rogue router advertisements.
Document Your Network
It’s best practice to keep up-to-date documentation of your network with accurate network diagrams and IP address assignments. Part of this documentation process should include keeping records of NDP-related configurations, so you have a quick reference during emergencies.
Conduct Regular Audits
If you suspect abnormal configurations, you should also periodically review your NDP configurations across the network and perform intermittent network scans to detect unauthorized IPv6 nodes.
If you follow best practices and understand the most common NDP issues that you could encounter, you can keep your IPv6 network running smoothly.
Conclusion
Neighbor Discovery Protocol plays a major role in IPv6 networks, handling device communication and network management tasks. IPv6 adoption will continue to grow, making understanding NDP more important than ever. Once you are comfortable with NDP, you'll be able to maintain and troubleshoot IPv6 networks more effectively as more organizations move towards this new standard.
Want to become a network expert? Consider our CompTIA Network+ Training!
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.