Mastering IGMP Snooping: Understanding and Implementing Multicast Efficiency

Quick Definition: IGMP snooping is a networking feature that allows switches to manage multicast traffic by monitoring IGMP messages. It helps reduce unnecessary traffic, improves security, and optimizes networking traffic.
When it comes to networking, network performance is the name of the game. IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) snooping is key to reducing network congestion, enhancing security, and improving overall network performance.
In addition to being important for overall network health, it's also a concept you'll need to understand to pass the Network+ certification exam. Below, we'll explore what IGMP snooping is, how it works, and how to implement it successfully.
What is IGMP Snooping?
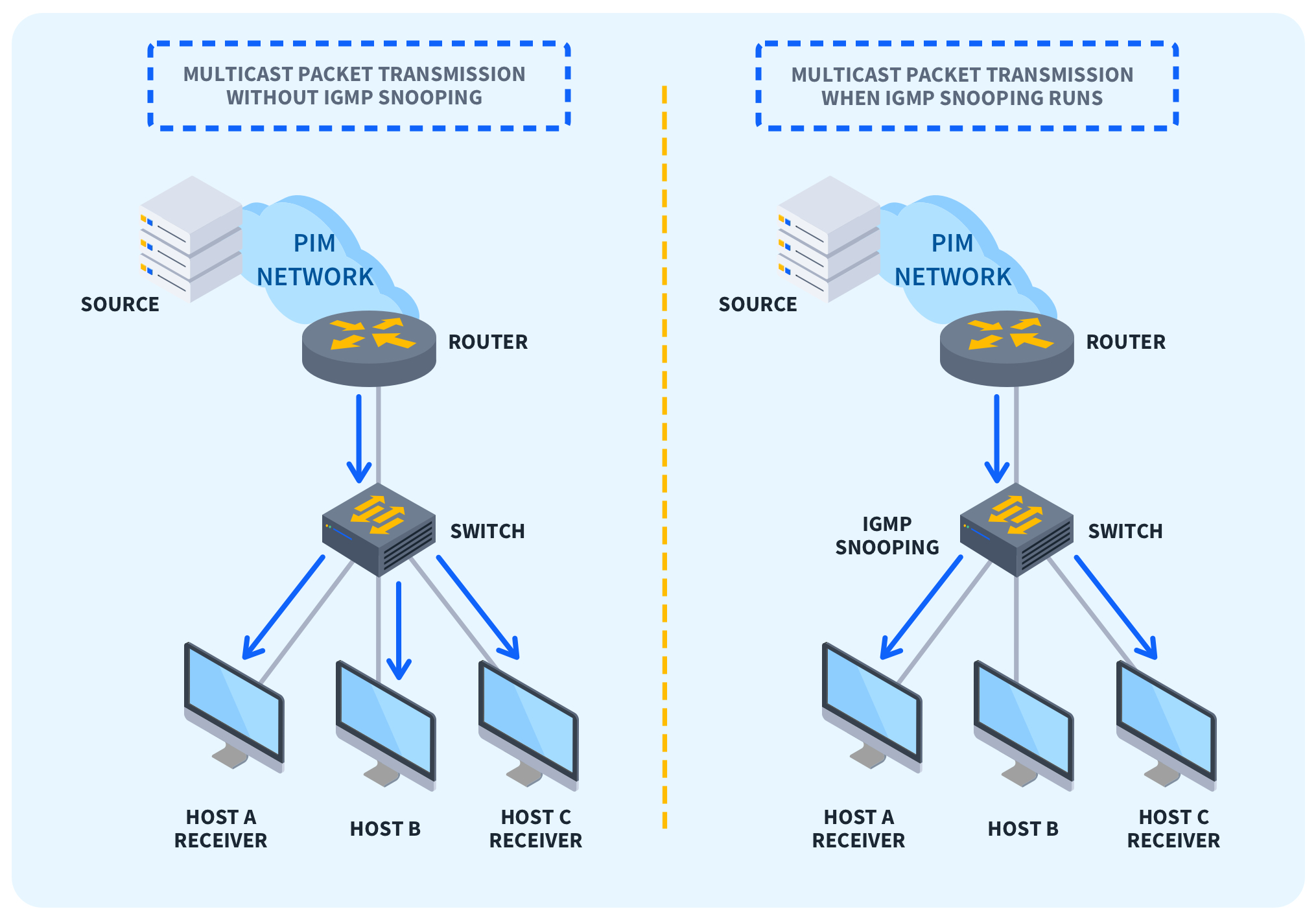
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping is a feature commonly found in network switches. It's primarily used in multicast environments where multiple devices receive the same data stream simultaneously. Multicast groups are basically a group of computers that have the same network traffic.
IGMP snooping helps optimize multicast traffic with a Local Area Network (LAN), enhancing efficiency and bandwidth utilization. IGMP snooping becomes critical in scenarios where careful management of bandwidth is required. It allows several devices to use the same IP address so they can receive the same data.
How IGMP Snooping Works
IGMP is used to manage host memberships and routing devices in a multicast group. IGMP snooping controls these multicast groups through snooping and analyzing multicast packets exchanged between upstream devices and downstream hosts.
IGMP works through monitoring and management of multicast traffic within a LAN. Multicast packets face issues traveling through Layer 2 switches of a LAN between the router and the multicast user. Multicast traffic by Layer 2 switches is dealt with as broadcast traffic, which is highly inefficient and can create security risks.
The cause of this inefficiency lies in the inability of switches to learn MAC addresses, resulting in multicast packets being broadcasted to all hosts, which is a waste of bandwidth and a threat to information security.
IGMP snooping restricts the flooding of IPv4 multicast traffic on a device’s VLAN. Once IGMP snooping is enabled, switches listen to IGMP network messages exchanged between hosts and routers. These messages include join and leave messages indicating which host wants to leave which multicast group.
Based on this information, IGMP builds a forwarding table and forwards only the traffic where group members are interested in a specific multicast content.
Does Multicast Work Without IGMP Snooping?
Yes, multicasts can definitely work without IGMP snooping but at the cost of efficiency and optimization of multicast traffic. Without IGMP snooping, multicast traffic by Layer 2 switches is dealt with like broadcast traffic, meaning they forward multicast packets to all hosts within a port irrespective of the interests of the host.
The absence of IGMP snooping can create network congestion due to inefficient and unoptimized multicast traffic. It also hampers the security of the network, as sensitive information can be exposed to unnecessary recipients.
Benefits of IGMP Snooping
We've already explored some of the benefits of IGMP snooping, including reducing congestion. Additional benefits include:
Efficient and Fast Network: IGMP snooping conserves bandwidth by reducing the amount of traffic forwarded by switches, making the network more efficient and faster.
Reduction in Traffic Flooding: If switches are unaware of which multicast group a device belongs to, it will forward the multicast traffic it receives, resulting in unwanted traffic. IGMP snooping resolves this issue by optimizing multicast traffic with a LAN.
Scalability: In large networks with numerous hosts, IGMP snooping ensures it targets only intended recipients, enhancing scalability by optimizing the traffic.
Enhanced Security: When multicast packets are broadcasted to all recipients, it creates an information security risk as sensitive information might be broadcasted to unintended recipients. IGMP snooping mitigates this risk through selective forwarding of multicast traffic.
When Should I Enable IGMP Snooping?
IGMP snooping should be enabled when a network is using multicast applications like online conferences, gaming, and video streaming. IGMP improves the management of multicast groups and helps optimize traffic. Moreover, if bandwidth and resource optimization are critical for your network, enabling IGMP snooping will reduce unnecessary traffic and help create resource-efficient networks.
We also enable IGMP snooping when a network involves multicast routers; in this case, IGMP snooping ensures compatibility and delivery of multicast traffic to intended recipients. Check out this course for an understanding of IGMP Snooping implementation.
How to Configure and Troubleshoot IGMP Snooping
The process to enable IGMP snooping can vary based on the device and its operating device/software. The general steps for enabling IGMP snooping on common devices are as follows:
Run System view, run IGMP snooping enable option. IGMP snooping is enabled globally.
After this, Run VLAN ID and enable multicast forwarding mode, by default, it will be set to IP address-based or MAC address-based forwarding
Run IGMP Snooping and enable it in the VLAN, this is to be done by running vlan { vlan-id1 [ to vlan-id2 ] } &<1-10> command in the system
Run Quit and return to system view.
Run WLAN, the WLAN display will be displaced.
Run Traffic Profile Name, Traffic Profile name will be displayed
Troubleshooting IGMP Snooping
Troubleshooting IGMP snooping involves identifying and resolving problems related to multicast traffic and IGMP snooping functionality. If you're having issues you think might be related to IGMP, follow these steps:
Check the IGMP snooping status and ensure the switch is turned on.
Next, verify VLAN configurations and check the IGMP snooping table.
Verify that the multicast router is properly configured and verify the IGMP functionality.
Check that devices participating in multicast traffic are correct members of VLAN.
Switch configurations also need to be checked for any misconfiguration-related issues.
Confirm that IGMP messages are not being blocked or filtered by firewalls and other security features.
Best Practices for IGMP Snooping
Implementing IGMP snooping involves following best practices to reach optimal performance. Here are a few best practices to keep in mind:
Ensure that IGMP snooping is enabled globally.
IGMP snooping should be enabled for appropriate VLAN
Update all network devices with the latest firmware to address all malware and bugs.
Designate a switch as the IGMP Querier to resolve IGMP Queries in the absence of a multicast router.
Validation of IGMP Snooping functionality should be done through testing of multicast applications.
Conclusion
IGMP snooping is a critical feature of network switches. Once enabled, it will optimize the handling of multicast traffic with LAN, resulting in enhanced network efficiency, reduction in bandwidth consumption, and a more responsive and scalable infrastructure.
To further understand and learn about IGMP Snooping, view this course on CBT Nuggets: IPv4 Multicast Fundamentals.
Not a CBT Nuggets subscriber? Sign up today and start learning.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.