What is DDNS and How Does It Work?

Quick Definition: Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) is a service that allows you to map a dynamic IP address to a static domain name, providing a constant hostname for a resource with a frequently changing IP address.
Have you ever needed to connect to your home computer from a remote location, but you don’t know your IP address? Maybe you’ve noted your IP address previously, but now it won't connect, even though the IP address seems to be online. It looks like your ISP has changed your IP address. How can you get around this without forking over extra money for a fixed IP address?
DDNS (Dynamic DNS) is the answer! It allows your server, desktop computer, or any other externally facing device to map its ever-changing IP address to a fixed hostname. This means if your Internet Service Provider has an automatic IP address policy that changes often, you and your users can find your server by remembering a simple hostname.
We'll look at what DDNS is, briefly examine its key benefits, how to set it up, and even some troubleshooting tips. Grasping the concepts of DDNS is vital for anyone looking to host websites, access devices remotely, or allow client connectivity to private networks.
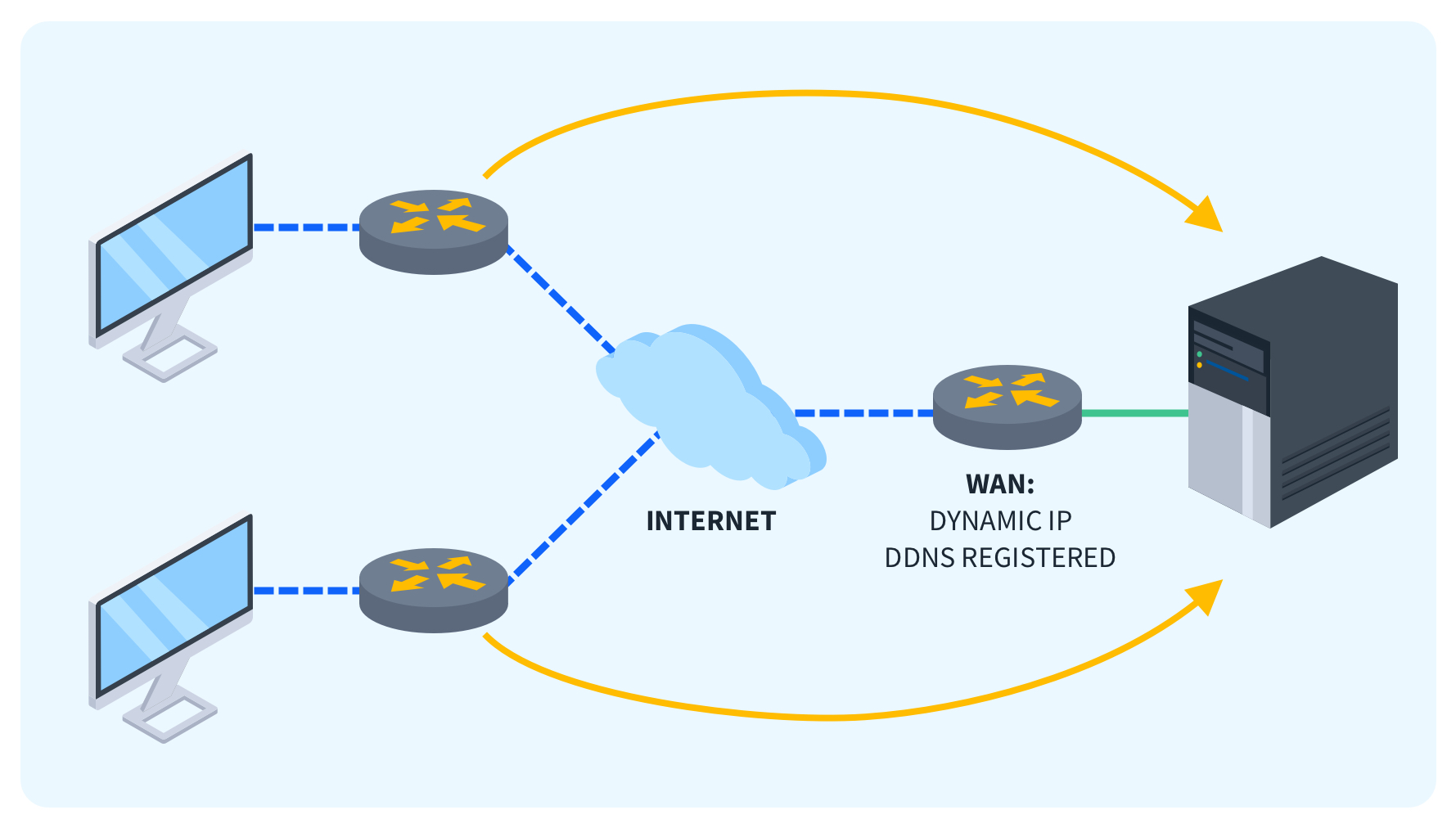
What is DDNS?
DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) is a service that maps IP addresses to static hostnames, which is especially useful for IP addresses that change often. Traditional DNS servers maintain static hostname-to-IP address mappings that rarely change. This works great for corporate companies with the resources to pay for a set IP address, but fixed IPs are often more expensive than a standard home-based internet connection.
What are the Benefits of DDNS?
Why would you use a DDNS? Below is a list of advantages and features that make DDNS such a popular service.
Remote Access: DDNS allows you to connect to devices on your home or office network remotely over the internet. You can access file shares, RDP, VPNs, and other services that require remote connectivity by using the hostname instead of remembering new IP addresses every time it changes.
Dynamic IP Management: DDNS handles dynamic IP changes seamlessly without any intervention from the user. The domain name will continue to resolve correctly after IP renewals, making it undetectable to your users.
Web Hosting: DDNS is essential for hosting websites and web services on dynamic networks, which is why visitors can use a website set up with DDNS without interruptions due to IP changes.
IoT/Device Control: Many home automation devices like security cameras only work with DDNS, which allows you to access them remotely using a domain name configured for them.
Improved Security: Accessing resources on private networks securely using VPNs, SSL, and other services is much easier when you have a static hostname you can connect to.
How to Set Up DDNS
It sounds complicated, but DDNS is very easy to set up. Setting up DDNS involves registering for a DDNS service, installing client software, and configuring your router:
Select a DDNS Provider: Some popular options are No-IP, ChangeIP, and CloudDNS. Choose one and create an account. Every service is slightly different, so you'll need to follow the installation instructions provided by the service.
Install DDNS Client: Download and install the DDNS client software provided by your service on your PC. This is usually a small installation file that installs the agent application on your computer. Its main function is to check your external IP address and notify the DDNS service of any changes, which it then maps to your hostname.
Configure Router: From the router admin interface, enable DDNS and enter your DDNS account details to link it. This is the most reliable way to ensure that your DDNS is always updated, because if your computer is powered off, then the DDNS client application will not be able to update your DDNS service in the event of an IP address change.
Update DNS Records: The client will automatically update your DNS records each time your public IP changes, giving you a fixed hostname that you can connect to with your configured applications.
Access Remotely: You can now access resources on your network remotely using the registered domain and applications. You'll need to set up port forwarding for some applications, services, and devices you want to reach from outside your local network.
How to Troubleshoot DDNS Issues
Even though the setup of a DDNS is relatively straightforward, sometimes issues arise that you might have to deal with. These include:
Cannot access a device remotely: If you can’t connect to your remote device, you will want to start with some basic troubleshooting. Start by verifying the DDNS setup and settings and your router port forwarding rules. Sometimes, a simple router reboot is all that is needed, while in other instances, you might want to give your client device a restart if needed.
Incorrect IP shows on lookup: If everything appears to be running correctly, but your IP address is not reflected in the application after an IP change, then you can look at the DDNS client logs. Again, simply restarting the client device or just the application is usually enough to kick-start the update process if the IP isn't updating.
Connection timeouts: If you are experiencing poor connectivity or frequent disconnects, start with the basics. Confirm your internet is indeed working and that there is internet connectivity. If this is your first time testing the service, then you may want to check if your ISP blocks DDNS ports by default. You can reconfigure your application to use alternative ports if they are blocked, or you can request that your ISP enable them so that you can get your DDNS up and running.
Authentication failures: If you have installed the service on your router, then be sure to double-check that the DDNS username and password are correct. Sometimes, you might want to log into the DDNS service provider’s website with your account and reset your credentials if you have exhausted all the other steps.
Unreliable access: Most DDNS services are free to get started with, which is a good way to find the right service for your needs. You can switch DDNS providers if one service is frequently failing or not connecting.
If you have tried all of these basics, then check out your DDNS provider's troubleshooting guides for additional debugging steps. If you are on a paid plan, you can contact their support to see if there is anything else you can try to get the service working as it should.
Final Thoughts on DDNS
So there we have it, DDNS explained with easy configuration and troubleshooting steps. Once you set it up, you'll quickly realize why DDNS is essential for many home users and small businesses offering remote services. By mapping dynamic IP addresses to static domain names, DDNS provides connectivity and accessibility for your specific needs.
The fundamental skills you will learn from getting certified with CompTIA’s Network+ will help you better understand all the basic concepts that underpin solutions like DDNS, which will make you a better IT pro!
If you have never had the opportunity to look at DDNS, hopefully, this will inspire you to try it, even if it is just a technical exercise. Think of a service you would like to set up and see if you can access it from your smartphone when you're not at home or share file access with friends and family.
Not a CBT Nuggets subscriber? Sign up for a 7-day free trial.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.