What is Channel Bonding?

Quick Definition: Channel bonding combines multiple internet connections for increased speed and reliability. It's ideal for network engineers and businesses with high data traffic, to deliver smooth, efficient operations.
The need for faster and more reliable internet connections is crucial in today's hyper-connected world. Channel bonding, also known as link aggregation or broadband bonding, is a technology that addresses this demand by combining multiple network connections into a single, unified pipeline. This innovative approach enhances your internet speed and offers numerous benefits, making it an enticing solution for individuals and businesses alike.
This article delves into the intricacies of channel bonding, including how it works, the benefits, and when you should use it.
What is Channel Bonding?
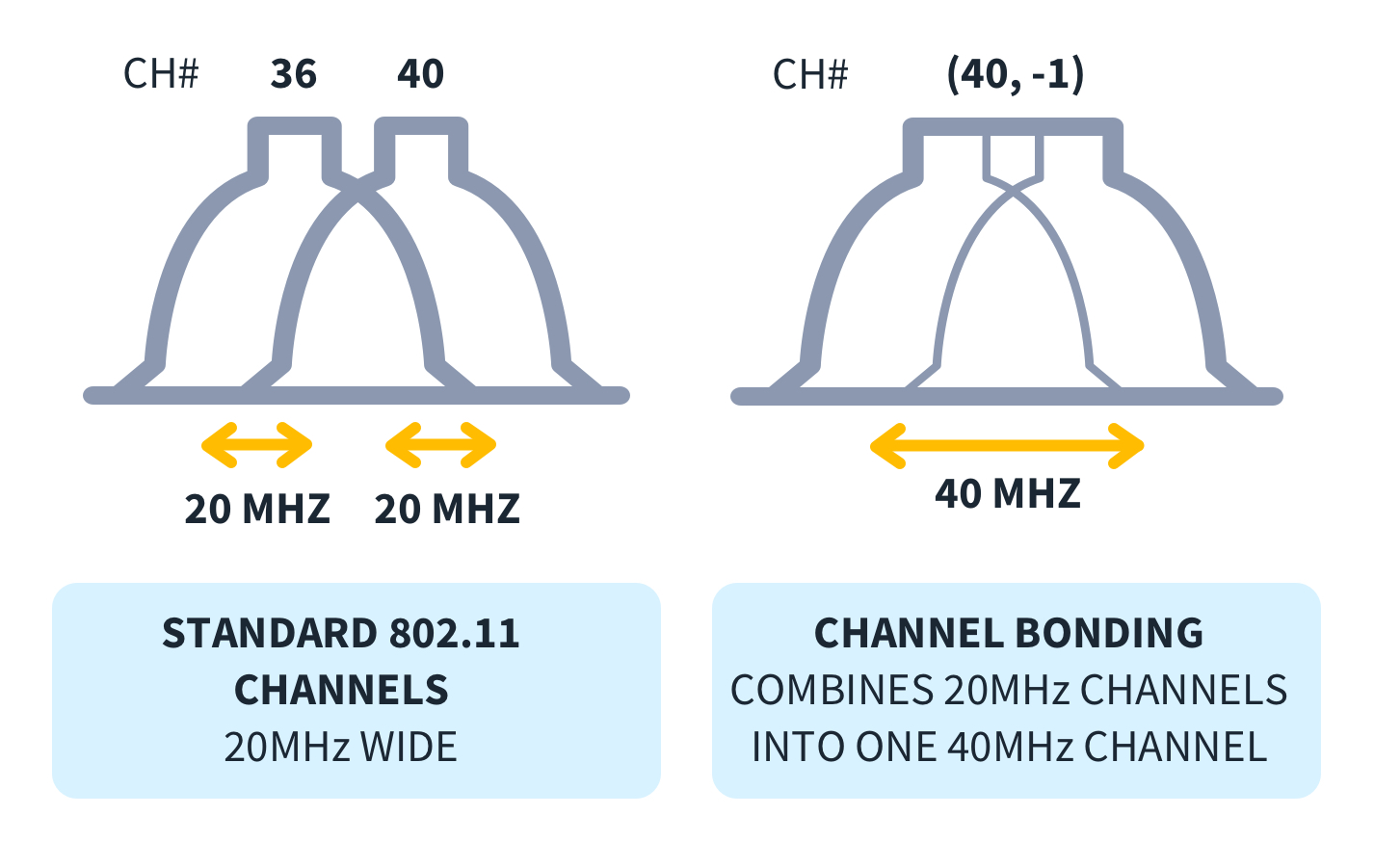
Channel bonding is a powerful technology that combines multiple internet connections to create a supercharged network. Leveraging these connections' combined bandwidth and resources significantly increases speed and reduces latency, making it ideal for demanding online activities. One of the key techniques used in channel bonding is upstream channel bonding, which combines multiple upstream channels to increase the data rate for uploads.
As a network engineer working for a company that relies heavily on internet connectivity, you’re responsible for ensuring its network is always up and running and fast enough to handle all the data traffic. Channel bonding can help.
Say your company moves a significant portion of its operations to the cloud. This means more data is transferred over the internet, increasing the demand on your network. You notice that during peak hours, the network struggles to keep up with the demand, leading to slow data transfers and frustrated users.
Or perhaps you’re setting up a remote office. The location is great, but it’s in an area with limited internet connectivity. In both these scenarios, channel bonding can be a powerful tool for a network engineer.
Channel bonding combines multiple network connections into a single, high-speed “superhighway” for your data. With channel bonding, think of each lane as a separate network connection. Each one can carry a certain amount of data, but when you combine them, you massively increase the overall capacity. No more data traffic jams!
How Does Channel Bonding Work?
Channel bonding works much like a multi-lane highway. By combining multiple network connections, or ‘lanes,’ channel bonding increases the overall capacity of your ‘highway,’ allowing more data to flow through at once. This is where the concepts of upstream and downstream channel bonding come into play.
Downstream channel bonding is like adding more lanes to your highway for incoming traffic. It combines multiple incoming network connections to increase the download speed. You receive more data at once, making activities like streaming videos or downloading files faster and smoother.
Upstream channel bonding is like adding more lanes for outgoing traffic. It combines multiple outgoing network connections to increase the upload speed. Upstream channel bonding is particularly beneficial when sending large amounts of data, like uploading videos or backing up files to the cloud.
Channel bonding doesn’t just blindly dump all data onto this superhighway. It intelligently distributes the data packets across the available lanes. Each packet of data, whether it’s upstream or downstream, is sent down the fastest route available at that moment.
Role of Specialized Hardware or Software
Achieving channel bonding typically requires specialized hardware or software. This could be a specific modem or router that supports channel bonding or a software channel bonding solution that manages data distribution across multiple connections.
This hardware or software is crucial to managing the channel bonding process. It’s responsible for splitting up the data, sending each packet down the appropriate connection, and then reassembling the data at the other end. Without this specialized hardware or software, channel bonding wouldn’t be possible.
Channel Bonding Vs. Other Technologies
It's important to distinguish between channel bonding and other technologies that can improve internet performance:
DOCSIS Bonding: or Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification bonding, is a bit like upgrading your cable TV package to get more channels. It’s a standard cable modems use to combine multiple downstream and upstream channels, effectively increasing internet speed. With DOCSIS bonding, you’re combining multiple smaller pipes into one larger pipe, allowing more data to flow through simultaneously. Unlike channel bonding, which can use any internet connection, DOCSIS bonding only works with cable internet connections.
NIC Bonding: This term refers to bonding multiple network interface cards (NICs) within a single device, increasing its throughput but not necessarily its internet speed. Think of it this way: each network interface card in a device is like a bridge over a river. The more bridges you have, the more traffic you can handle at once, and the less likely it is that any single bridge will become a bottleneck. Unlike channel bonding, which combines multiple network connections, NIC bonding combines multiple network interface cards within a single device.
Benefits of Channel Bonding
Channel bonding increases speed, as we've discussed. But there are several other benefits to using this technology, including:
Increased Bandwidth: The primary benefit of channel bonding is undoubtedly the significant increase in bandwidth. This translates to faster download and upload speeds, allowing you to transfer large files, stream high-definition content, and participate in online activities without lag or interruptions.
Improved Reliability: Using multiple connections, channel bonding provides redundancy and minimizes the impact of individual connection failures. This ensures a more reliable and stable internet experience, even during peak times.
Reduced Latency: Latency refers to the delay in data transmission, which can affect online gaming, video conferencing, and real-time applications. Channel bonding significantly reduces latency, leading to a smoother and more responsive online experience.
When to Use Channel Bonding?
Channel bonding is particularly beneficial for individuals and businesses with demanding online needs, such as:
Businesses With Heavy Internet Usage: Businesses that rely on cloud-based applications, frequent file transfers, and video conferencing can significantly benefit from the increased speed and reliability provided by channel bonding.
Rural or Underserved Areas: In areas with limited internet access options, channel bonding can combine multiple slow connections for a significant speed boost and improved internet experience with channel bonding.
Online Gamers and Streamers: For gamers and streamers who prioritize low latency and high bandwidth, channel bonding offers a powerful solution for achieving a competitive edge and a more enjoyable online experience.
How to Implement Channel Bonding
There are two primary ways to implement channel bonding:
Hardware: Many routers, switches, and modems support channel bonding functionality natively. This requires purchasing and configuring a compatible device to bond your internet connections.
Software: Software solutions like Speedify and Connectify Hotspot offer a more flexible and cost-effective alternative for channel bonding. These applications can be installed on your computer or mobile device, enabling channel bonding without requiring specialized hardware.
To implement channel bonding, start by assessing your network setup. Identify the network connections you want to bond, such as Ethernet connections, cable connections, or other network links. Then, refer to your device's user manual for directions on how to set up channel bonding.
Most will require you to log in to your router or networking device's management interface and locate the channel bonding settings. If you choose to use software, follow their directions to implement it.
Limitations and Considerations for Channel Bonding:
While channel bonding offers significant benefits, it's important to consider the following limitations:
Multiple Internet Connections: Channel bonding requires at least two internet connections, which may not be feasible for everyone.
Device Compatibility: Not all devices support channel bonding, so you may need to upgrade your hardware or software.
Technical Expertise: Setting up channel bonding can be technically challenging for the average person and requires some network configuration knowledge.
Bonus Tips to Make the Most of Channel Bonding
Channel bonding is a powerful tool for network engineers to improve network performance. Before implementing it, however, you should keep a few tips in mind.
Explore Free Options First: Consider channel bonding software solutions like Speedify that offer free trials or limited free plans. This will allow you to see how it impacts performance before investing in more expensive options.
Monitor Performance: Regularly check your network performance to identify and address any issues.
Test and Experiment: Don't be afraid to try different combinations of connections and configurations to find the optimal setup for your needs. And keep in mind, your needs may change over time.
Final Thoughts on Channel Bonding
Whether you’re a network engineer managing a company’s internet infrastructure, an online gamer in a high-stakes tournament, or a business professional conducting a crucial video conference, channel bonding can be a game-changer. It’s like merging several small streams into a mighty river, unlocking the full potential of your bandwidth and leading to faster speeds and a smoother online experience.
Channel bonding can significantly enhance your network's speed and reliability by combining multiple connections, such as your home’s DSL and mobile LTE connections. Channel bonding is a powerful tool worth considering, no matter who you are or what your online needs are. It has the potential to revolutionize your internet experience, turning a choppy, lagging connection into a supercharged highway of data.
Not a CBT Nuggets Subscriber? Sign up and start learning today.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.