VRRP vs HSRP: What are the Differences?

Quick Definition: VRRP is an open standard protocol, while HSRP is Cisco-proprietary. However, both are essential for network reliability, allowing for automatic failover in the event of hardware failure.
In networking, reliability is king. Solid switching and rock-solid wifi, while important, are worthless if another key component fails: your router. Two protocols can save the day: VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) and HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol).
They both provide fault tolerance in the event of a failed router, upping the level of resiliency for your network. Let's take a deep dive into these protocols, the features and advantages of each, and which might be a better choice for your needs.
What is VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol)?
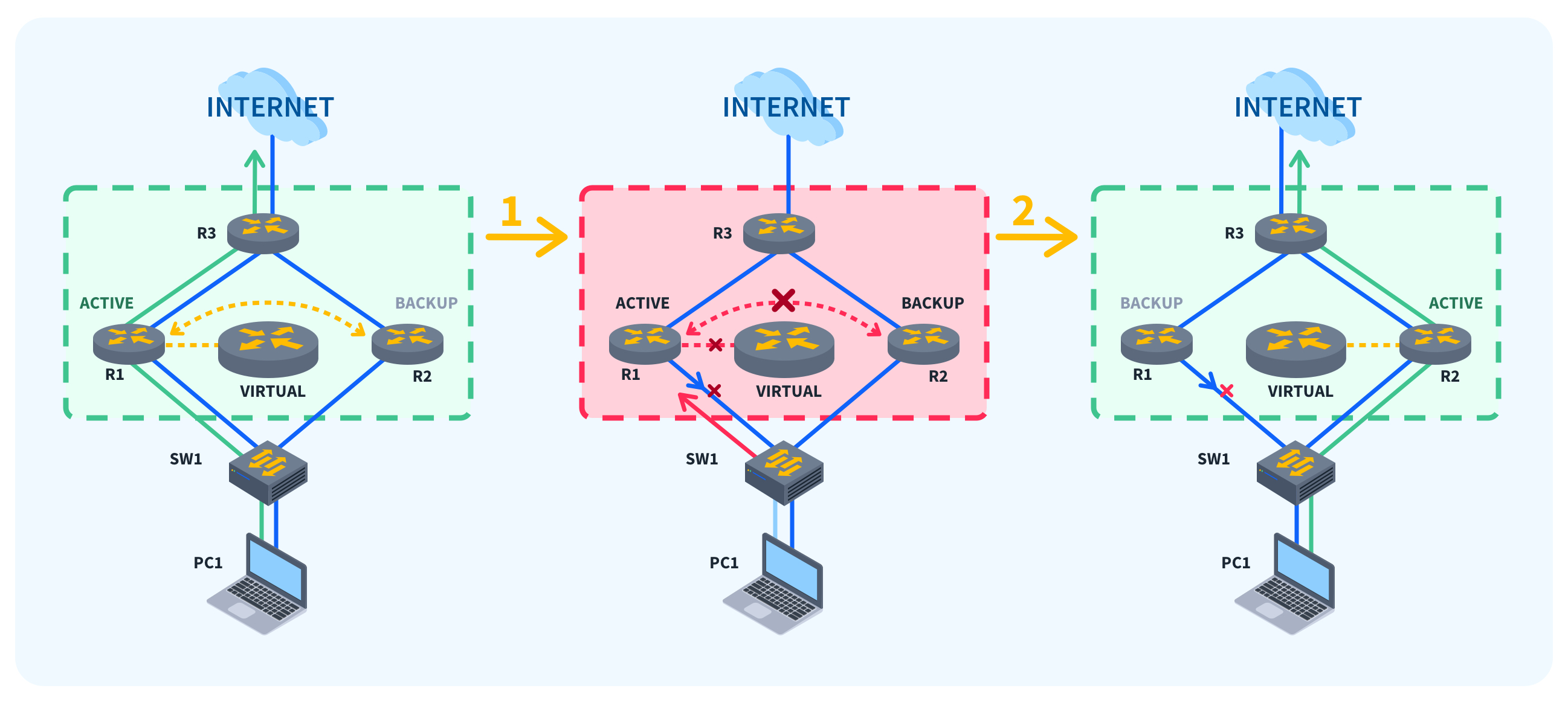
VRRP is an open, industry-standard protocol for router redundancy. It works by creating a virtual IP address to be used by the network as the default gateway (aka, the host to go to to get out of the LAN and onto other LANs or the internet). Multiple routers are configured as a VRRP redundancy group.
One router is designated as the primary router, and it assumes the virtual IP address. This router will broadcast its MAC address when an ARP request is sent on the network from a host trying to find the gateway IP. (As a quick reminder, an ARP request is when a device broadcasts, "Who on the network has this IP address?" and the other device responds, "I do, my MAC address is…" The first device can then send packets to the second device.)
The group of routers communicate with each other via multicast, sending advertisement messages to keep up with what other routers are live on the network. If enough routers see that the primary router is not responding, they assume it is offline, and the standby router takes over, responding to ARP requests for the virtual IP with its MAC address. Your users shouldn't see more than a few seconds of downtime.
Advantages and Disadvantages of VRRP
VRRP offers a huge advantage in situations where network connectivity is critical. In businesses where downtime can cost thousands of dollars or more per minute, keeping the network online and healthy is worth the time and effort to implement routers capable of using VRRP for device redundancy and automatic failover in the event of a failure.
Another huge benefit of VRRP is load balancing. If the router manufacturer implements it in their devices, your VRRP setup can also be used to balance traffic between two routers, increasing your available bandwidth. This is especially helpful when doing deep packet inspection or other CPU-heavy traffic processing, and a single router just can't keep up.
To accomplish load balancing, the primary router will respond to ARP requests in turn with the MAC address of itself and the standby router, effectively splitting the traffic between the two devices.
One requirement (and possible disadvantage) that might or might not be obvious for using VRRP is that all routers in a redundancy group must be on the same LAN and on the same subnet as the hosts. If a host can't reach a standby router, then the redundancy is useless, so every router must be connected to the LAN physically via switches and logically via VLANs (if relevant for your network).
What is HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol)?
HSRP is a closed proprietary protocol created by Cisco. It is very similar to VRRP in that it is used to provide greater network reliability by using multiple routers for redundancy, one as active and the other as standby. Health monitoring between the two allows the standby to become active if the original active router stops responding.
While some Cisco routers do support VRRP, HSRP is only available on Cisco routers. Cisco created HSRP as its only proprietary implementation of a router redundancy protocol. HSRP works by assigning a priority value to each router in a group.
The routers communicate using Hello messages to find each other. By default, the router with the highest priority is set as active, and all others are on standby. If that router fails, the next highest-priority router becomes active.
Advantages and Disadvantages of HSRP
Similar to VRRP, HSRP's main advantage is high network availability, though it works a bit differently. It also creates a seamless failover by quickly switching to a standby router if the active router doesn't respond quickly. We'll explore the drawbacks to HSRP in the next section, but the core drawback is that HSRP doesn't offer true load balancing on its own.
Differences Between VRRP and HSRP
One significant difference between HSRP and VRRP is that HSRP does not create a single virtual IP for the routers in the redundancy group. With VRRP, both routers have separate, unique private IPs. A common implementation is that one router is active, and its LAN interface has an IP used by hosts on the network, 192.168.1.1, for example.
The standby router also has its own IP, like 192.168.1.2. If the standby detects that the active is offline, the standby takes over the 192.168.1.1 IP address and becomes active. All network hosts failover to the standby router with minimal downtime.
Load balancing is also slightly different. Where VRRP has true load balancing, with traffic split between the two devices, HSRP can only do load sharing. Since both routers have a unique IP, different hosts can be configured to use either one. This becomes problematic if either goes offline, as a subset of your hosts now can't reach their gateway. For this reason, load sharing isn't typically implemented, as it can create more problems than it solves.
Cisco does make up for this, however, with another proprietary protocol: GLBP. The Gateway Load Balancing Protocol uses a scheme very similar to VRRP, with a single virtual IP address for all the routers and different ARP replies to balance between them. In fact, the redundancy mechanism of GLBP is also nearly identical to VRRP, with routers communicating via multicast for health checks and a standby taking over for a failed active.
How to Choose the Right Protocol: VRRP vs HSRP + GLBP
Choosing the right protocols for router redundancy and load balancing comes down to one key question: are you in a Cisco environment or not? The functionality between VRRP vs HSRP and GLBP is so similar that implementing either will provide the redundancy your network needs.
Doing things "the Cisco way" is usually safest when using Cisco hardware, so if that's your situation, go with the proprietary protocols. If you're using any other brand, go with VRRP.
Network uptime and reliability are essential. These redundancy protocols are key players in optimizing the reliability of your networks. Whether it's the open VRRP protocol or Cisco's HSRP and GLBP, implementing either will pay dividends when downtime is costly.
Want to learn more? Explore CBT Nuggets' IT certification training.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.