What is ToR (Top-of-Rack) Switching?

Quick Definition: Top-of-rack (ToR) switching is a network architecture in which switches are placed at the top of each server rack in a data center, providing direct connections for the servers within.
Picture your data center's network as a sprawling highway system, where servers and devices are like individual cars moving vast amounts of data. In this scenario, Top-of-Rack (ToR) switches function as strategically placed highway exits.
They provide dedicated access points for the cars (servers) within a localized area (the server rack). This approach streamlines traffic flow, minimizing congestion and ensuring smooth data transfer within modern data centers.
What are the Key Components of Top-of-Rack (ToR) Switching?
In traditional data centers, cables can become a tangled mess, slowing down data and making management difficult. Top-of-rack (ToR) switching solves this problem by placing network switches directly within server racks. This approach streamlines connections, improves performance, and makes your data center easier to manage.
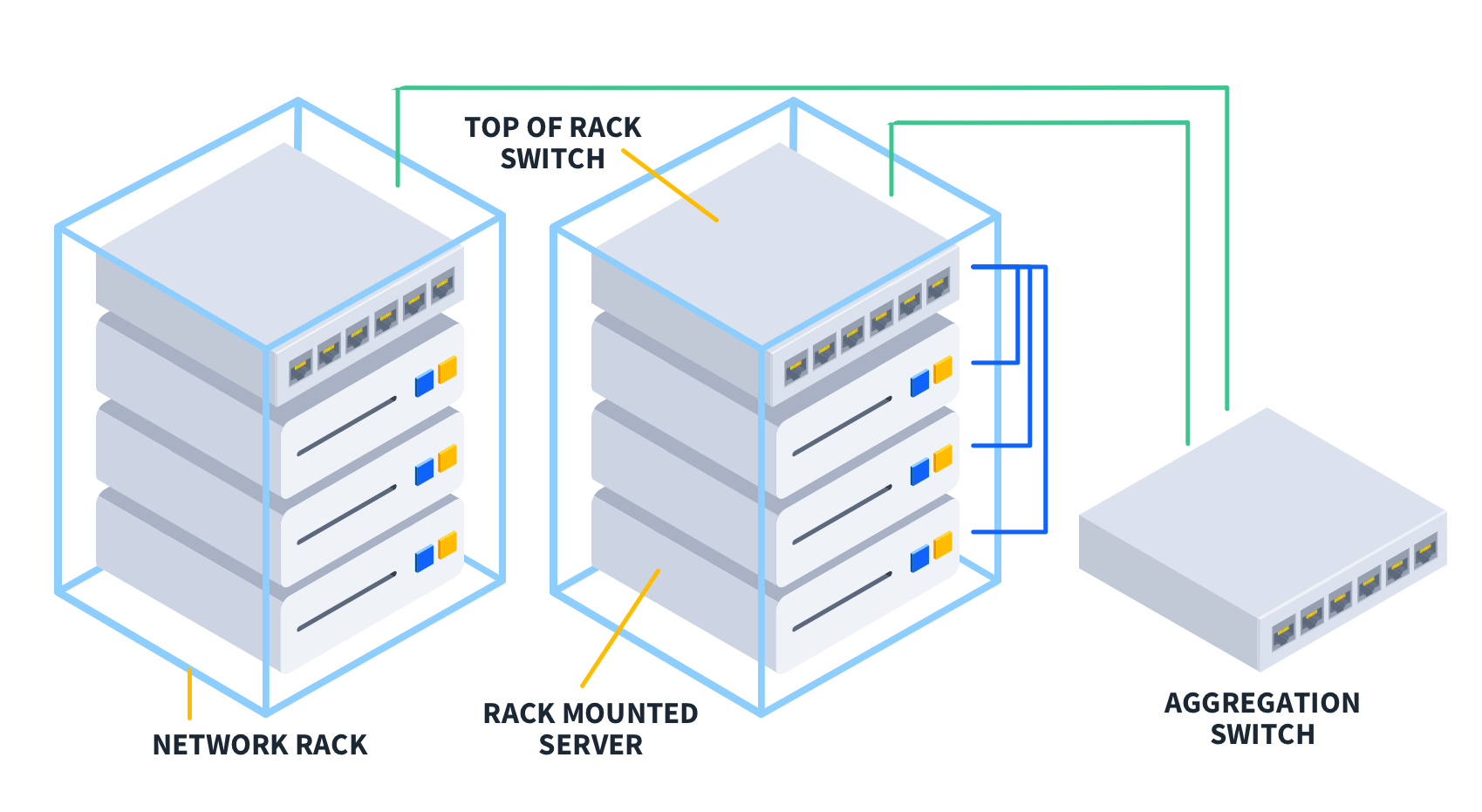
There are two main components of ToR switching, including:
ToR Switches
Top-of-rack (ToR) switches are specialized network switches designed to fit at the top of server racks. Think of them as highway exits tailored to a specific area. These switches are compact, feature a high density of fast network ports (10GbE, 25GbE, 40GbE, 100GbE), and are optimized for fast, low-latency data forwarding.
Top-of-rack (ToR) switches efficiently handle two crucial tasks:
Aggregation: They consolidate traffic from multiple servers within the rack.
Forwarding: They direct traffic between servers within the rack and to other parts of the network via connections to higher-level switches.
Server Connections
These are the direct links established between the ToR switches and the servers within the rack. Just as exits provide direct access to and from the highway, top-of-rack (ToR) switches establish direct links to servers using short cables. They help organize the network setup, reduce data transfer delays (latency), and make it easier to add or remove servers without disrupting the entire network.
What are the Advantages of Top-of-Rack (ToR) Switching?
Top-of-rack (ToR) switching introduces a streamlined, localized approach to data center network design. It establishes direct server connections by placing dedicated switches directly within each server rack. This offers several benefits, including:
Streamlined Cabling and Reduced Clutter: The ToR approach is like localizing highway access. It avoids the need for every car (data packet) to travel long distances, simplifying your data center's overall 'road network' and improving organization.
Enhanced Network Performance and Reduced Latency: Direct server connections within the rack are like using local roads instead of always merging onto the main highway. This significantly reduces latency, benefitting applications sensitive to delays.
Scalability: When you need to accommodate more servers (cars), ToR switching allows you to expand 'local exits' as needed. Changes are contained, reflecting the on-demand nature of modern data centers.
Learn more about Cisco data center network design in our course CCNP Data Center Training - 300-610 DCID.
Challenges and Considerations in Top-of-Rack (ToR) Switching
Top-of-rack (ToR) switching offers significant advantages for data center networks. It streamlines cabling, reduces latency, and supports easy scalability to meet changing demands. However, to fully realize these benefits, it's crucial to address potential challenges.
These include managing multiple switches, ensuring load balancing and redundancy, maintaining consistency across ToR devices, and implementing strong security measures to protect this expanded network infrastructure.
Management and Configuration: When multiple ToR switches are in use, you will need centralized control over their settings. This means having tools and strategies to manage them all from a single point and ensure they are all configured consistently.
Load Balancing and Redundancy: To avoid bottlenecks and ensure smooth data flow, the workload must be distributed evenly across the ToR connections. Additionally, having backup switches in place (redundancy) ensures that if one switch fails, another is ready to take over, minimizing downtime.
Uniformity and Compatibility: Using the same model of ToR switch throughout the data center simplifies management. It ensures that configurations, troubleshooting, and maintenance procedures remain consistent across all switches, leading to more predictable network performance.
Security Considerations in Top-of-Rack (ToR) Switching: To ensure the safety of ToR switches, it's essential to follow best practices such as:
Install regular updates to keep the switches patched and protected against vulnerabilities.
Use strong passwords to prevent unauthorized access.
Implement access controls to limit who can make changes to the switches' configurations.
Consider network segmentation to add an additional layer of protection by isolating different parts of the network.
Integration with Network Virtualization and SDN
Top-of-rack (ToR) switches form the physical foundation for highly dynamic, virtualized data centers. They seamlessly integrate with network virtualization, which allows for the creation of flexible, software-defined networks.
Modern ToR switches often support software-defined networking (SDN), enabling centralized control and automated configuration through an SDN controller. This powerful combination allows your network to rapidly adapt and match the agility of virtualized workloads, which can be created, moved, or scaled on demand. Here's how they work together:
Alignment with Virtualization: ToR switches provide the physical infrastructure necessary for network virtualization. This technology enables the creation of customized networks on-demand, similar to building custom highways for data to travel within the data center.
SDN Integration: Modern ToR switches often support SDN. In this setup, ToR switches function as intelligent components within a software-controlled network. An SDN controller centrally manages these switches, automating configuration processes and dynamically adjusting traffic patterns as needed.
Agility and Programmability: By combining ToR switches with SDN capabilities, your network gains agility and programmability. This means the network can quickly adapt to changing demands, much like how virtual workloads within the data center can be created, moved, or resized on the fly.
Conclusion
Top-of-rack (ToR) switching is a cornerstone of efficient and adaptable data center design. The analogy of strategically placed highway exits highlights its core advantages.
By simplifying network infrastructure, reducing latency, and offering on-demand scalability, ToR switching empowers data centers to embrace flexibility. It also provides a robust foundation for virtualized environments, allowing your network to effortlessly match the ever-evolving demands of modern workloads.
Learn what IT Certification Training CBT Nuggets has to offer!
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.