Networking Basics: What are Wildcard Masks and How do they Work?

Quick Definition: A wildcard mask allows or denies all the traffic from a network IP address. It tells the router which bits in the IP address need to match the access list and which do not.
Let's say you want to get your car washed. You pull into the car wash, go up to the counter, and ask for the deluxe car wash. You don't realize it, but it comes with an air freshener.
The car wash clerk asks, "What type of air freshener would you like?"
You say, "One that freshens the air."
The clerk says, "No, what scent would you like?"
Because you weren't planning that far ahead, you say, "I don't care. Any of them."
Alternately, when the clerk asked you, "Which one do you want?" You could have responded, "None of them."
In either case, you either don't care (or care strongly enough to make a choice). That's exactly how a wildcard mask works. It tells the router which parts of the IP address it doesn't need to care about. (As much as a router can care, that is.)
What is a Wildcard Mask?
A wildcard mask is a mechanism used in access control lists (ACLs) to specify which bits of an IP address should be checked and which can be ignored. It determines which portions of the IP address must match exactly and which can vary, allowing for flexible and improved traffic filtering.
How Does a Wildcard Mask Work?
A wildcard mask identifies some portion of an IP address that we either care about or don't care about and grants either all or no access from that network. It's very black and white.
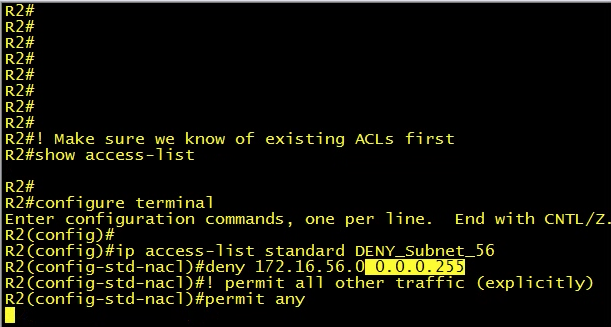
Let's say your manager says, "Too many people in Sales are using the nice printer in Finance. I want you to deny any traffic sourced from network 172.16.56.0." You can either individually filter every IP address in that network or create a wildcard mask to block everyone.
In this case, you're going to create an Access Control List that blocks the network 172.16.56.0, and any devices on that subnet.
In a subnet, the IP addresses for the printer and computer are the same, except for the last octet. That's because they're on the same network. The last number identifies the device. The first three identify the network.
Printer – 172.16.56.5
Computer 1 – 172.16.56.8
You can apply a wildcard mask that only looks at the first three octets, denying traffic from the entire network.
It doesn't matter what the bits in the last octet say as soon as the router only cares about the first three octets. If they're on the blocked list, then you're not getting through.
A wildcard mask tells the router which bits it should examine and which bits not to examine. It's an easy enough concept.
Wildcard Mask Example
If you need to create an access list that will deny everything from the 172.16.56 network but permit all other traffic, then see above.
deny 172.16.56.0 0.0.0.255Notice the wildcard mask. The wildcard mask is 0.0.0.255. With the wildcard mask, the IP address doesn't have to match; it could be anything.
Where Can Wildcard Masks Be Used?
Wildcard masks are beneficial when you have a large network and need to allow free traffic flow between multiple routers. If you have a large network with several routers and LAN segments, you will likely run into wildcard masks.
Just make sure you properly set your wildcard mask to ensure only allowable traffic can pass through your router.
When Not to Use a Wildcard Mask and Alternative Options
While wildcard masks are powerful tools in network configuration, there are scenarios where their use may not be ideal. Depending on the situation, there are several alternatives to consider.
Subnet Masks: In cases where simplicity matters, using subnet masks might be more straightforward. Subnet masks clearly define which portion of the IP address is the network and which is the host, making configuration more intuitive.
CIDR Notation: Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation provides a clear and concise way to specify IP address ranges without the complexity of binary calculations required by wildcard masks.
Access Control Lists (ACLs): When high security and specific control over traffic are required, setting ACLs using exact IP addresses or subnet masks can be more effective.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP): In networks where IP addresses are dynamically assigned, relying on wildcard masks can lead to unpredictable access controls. Using DHCP with proper subnetting reduces the risk of incorrect traffic filtering.
Routing Protocols: For complex networks with multiple subnets and routing requirements, using routing protocols like OSPF or EIGRP, which automatically handle subnetting and routing decisions, can be more efficient.
CBT Nuggets Wildcard Mask Training
Wildcard masks play a vital role in the smooth flow of network traffic. The CBT Nuggets training library features a wide variety of networking training from widely respected vendors such as Cisco and CompTIA. Our following courses address wildcard masks:
Keith Barker explains wildcard masks more in-depth here:
Want to try a CBT Nuggets course? Get a free 7-day trial.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.