How do Smart Devices Work?

Quick Definition: Smart devices are internet-connected gadgets, such as smart speakers and thermostats, that communicate with networks and other devices to perform tasks like remote control and automation.
Smart devices are everywhere. From homes to businesses, small intelligent devices are working tirelessly to keep our lighting, air conditioning, and security systems under our control. They offer us visibility, convenience, and security and are essential for staying connected.
Have you ever wondered how smart devices work or what kind of communication they need to work properly? We rounded up the most popular smart device standards and explained how they work so that you can understand how they should be positioned in your own network. It isn't always easy to cut through the branded jargon and proprietary protocols offered by different manufacturers, but we've got you covered.
Once you understand how they operate, you can plan and secure both corporate and home networks to allow for better performance and security.
What are Smart Devices? How Do They Work Within IT?
Smart devices come in many shapes and sizes, along with different features and capabilities. In general, a smart device is a device that has sensors, processing power, and internet connectivity all rolled into one. Some examples include:
Smart Refrigerators: These refrigerators monitor food levels, suggest recipes based on what's available in the refrigerator, and, if configured properly, even order groceries online.
Smart Speakers: These are devices like Amazon Echo and Google Home which use voice recognition as their input. They can play music, control other smart home devices, and provide information to basic search queries.
Smart Thermostats: Smart thermostats learn user preferences over time and automatically adjust home temperatures to match your ideal temperature and efficiency profile. They can be manually overridden when needed, giving you more control over your home's heating and cooling.
Smart Doorbells: Smart doorbells have become very popular in recent years as security devices that are also convenient ways to speak with visitors, even when you aren't home. Most have cameras and motion sensors that record when movement is detected so that you are aware of any visitors approaching your house or business.
Smart devices can be commanded directly on the device via buttons, a touch screen, or through a smart app. Others can work without supervision and help automate common tasks so that we don't have to do them ourselves, or they can be a combination of user-controlled and automated.
How Do Smart Devices Use Networks?
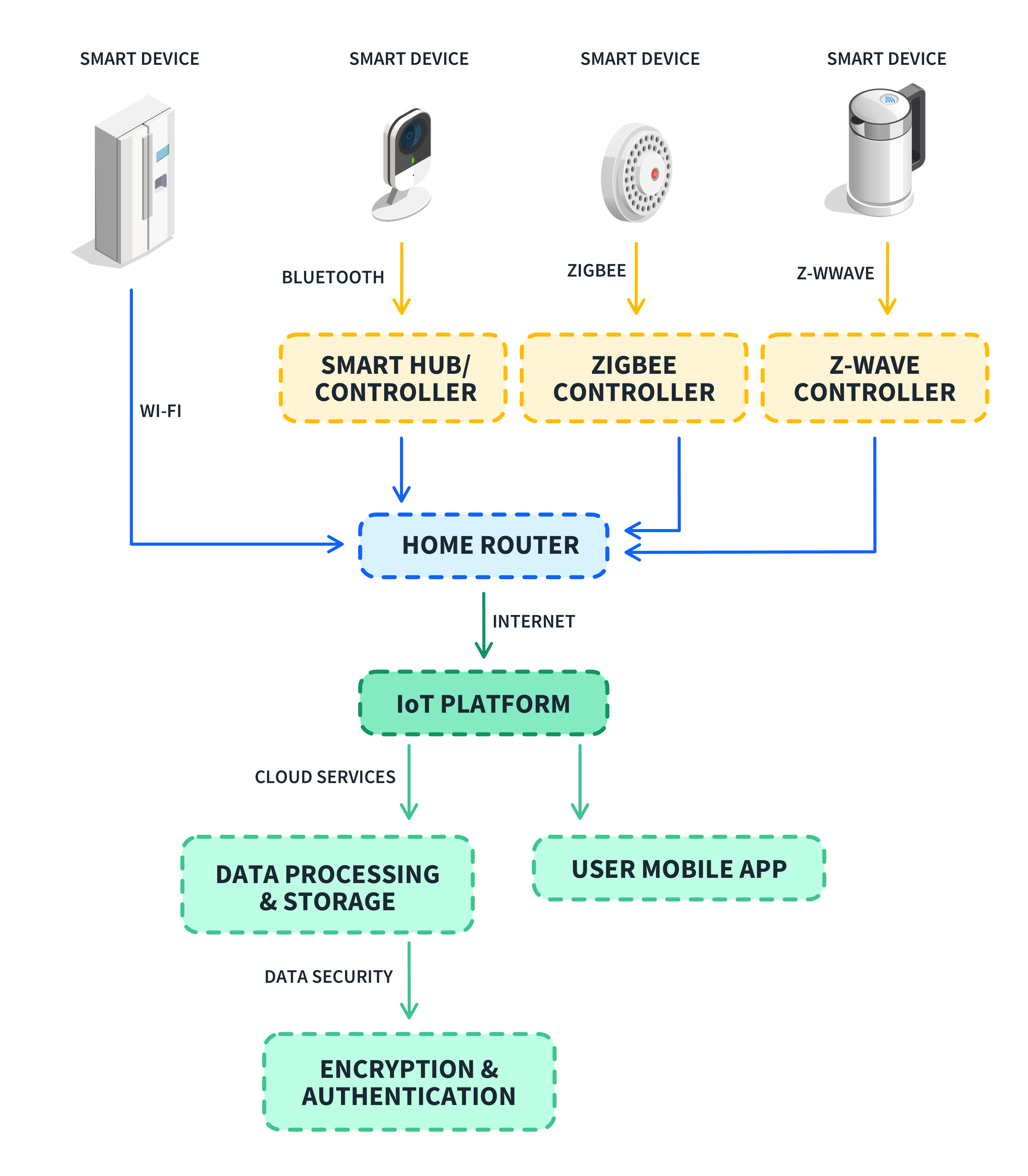
Smart devices rely on different connectivity standards to transfer data with other devices and networks. Different brands use different wireless communication protocols, with examples like:
Wi-Fi: We all know about Wi-Fi. It's the most common wireless networking standard used in homes and businesses. Many smart devices are Wi-Fi capable, giving them access to both local and internet-based resources like servers and other smart devices.
Bluetooth: Smart devices can use Bluetooth to communicate with one another, and can allow you to control them from a smartphone with Bluetooth capabilities. It is a short-range protocol and can only be used when devices are within range of one another.
Zigbee: A wireless mesh network standard designed for low-power, low-bandwidth communications. It is used by smart devices to communicate with a central hub, and with one another.
Z-Wave: Another wireless mesh networking protocol commonly used in home automation. It communicates with other smart devices and central controllers and hubs.
The Internet of Things (IoT) also plays a big role in smart device connectivity:
IoT platforms provide a way for smart devices to connect and communicate with each other and the cloud.
Cloud-based services enable remote access, data storage, and processing for smart devices.
The MQTT protocol is commonly used for lightweight IoT communication.
What Technology is Required to Make Smart Devices Smart?
A device must have various technologies and capabilities to be considered ‘smart. ' Below are some of the most common smart technologies currently found in devices.
Sensors: These are components that detect and measure the device's immediate environment, such as temperature, motion, light, and anything else that the device needs to detect or measure. When certain conditions are met, your device will start or stop an action or report on the environment with an alert. This is what makes the device seem almost magical, because it seems to act on its own without being prompted by us.
Actuators: These mechanisms can move or control a peripheral or a system, like automatically adjusting a thermostat, or activating a motor or speaker. They accept a signal from the smart device’s microcontroller and then apply changes to other components within the smart device.
Microcontrollers are small, low-power computers (similar to an Arduino) that can process data from sensors and control actuators or other components inside the smart device.
Some smart devices contain more powerful processing units (like a modern smartphone) so that they can perform more computationally intensive tasks like video processing in a smart doorbell.
Operating systems
Embedded operating systems are designed to perform specific tasks within a larger mechanical or electrical system.
Real-time operating systems (RTOS) can process data and respond to events in real time, which is crucial for smart devices that must act within milliseconds.
Linux-based operating systems are also commonly used in smart devices thanks to their flexibility and open-source status of Linux.
What are the Security Implications of Using Smart Devices?
Smart devices offer convenience and security, but they also come with some issues that we need to think about. Here are the security considerations to keep in mind when installing smart devices in your home or business:
Vulnerabilities in Smart Device Networks
Data privacy concerns: The massive amount of data collected by smart devices can create problems, especially if it contains personally identifiable information like email and physical addresses.
Cybersecurity threats: Any device that is connected to the internet is a potential target for hacking attempts that can monitor your internal network or deliver malware. To minimize this, you should secure these devices with strong passwords and also consider segmenting them on their own VLAN or WiFi SSID to minimize exposure to the rest of your network.
Encryption and authentication mechanisms
Encryption: This is critical for securing sensitive data transmitted by smart devices. If your devices have the capability to encrypt your data, you should enable it to secure your communications with them.
Authentication methods: Passwords or biometric data ensure that only authorized users can access your smart devices. If you have sensitive data like security camera streams, you should lock down and secure the applications you use to access these smart devices.
What are the Challenges You Might Experience With Smart Devices?
In addition to security challenges, which we've already covered, there is one other main challenge related to smart devices — compatibility.
With so many different brands and communication protocols, getting smart devices from different manufacturers to work together seamlessly can be a challenge. Not all smart devices are compatible with one another, so choosing additional hardware to add to your current environment requires research to ensure compatibility.
The Future of Smart Devices
As smart devices get smarter, their applications are increasing. Here are a few trends that may impact when and how we use smart devices.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning have become a selling point for many smart devices. As AI continues to mature and evolve, we can expect to see even smarter devices with enhanced autonomy in the future. Manual overrides and the ability to control these devices are important as we trust smart devices with more control over aspects of our daily lives.
Energy Efficiency
Low-powered electronics have been a game changer in energy efficiency, and improved battery life has made devices like smart vacuum cleaners far more useful as their operating times improve. Further battery development will continue to improve the performance and operating times of devices, and with home robotics looming on the horizon, batteries with efficient designs are going to be even more important.
Compliance and Standards
Smart devices are becoming more prevalent every year, which makes regulatory compliance and development standards critical to ensure security and reliability. Devices that operate within secure locations have to have certification and be validated as secure if there is a possibility of them operating on sensitive networks.
Use Cases and Practical Applications
To see how smart devices are being utilized in the real world, let's look at a few use cases:
Smart home automation systems like Samsung SmartThings allow users to connect and control a wide variety of smart devices from a single hub or app.
Industrial IoT solutions are merging with traditional industrial instruments that are giving manufacturers and production lines enhanced reporting and instrumentation. These help make more efficient manufacturing processes possible and allow for better resource planning and production.
In healthcare, smart monitoring devices can track patient vitals and send alerts to medical professionals if any concerning changes are detected. They also have the potential to detect medical conditions that might not have been diagnosed previously, making them especially beneficial for patient health.
Looking Ahead
As we've seen, smart devices rely on a combination of sensors, processors, connectivity standards, and operating systems to enable their intelligent capabilities. Understanding these underlying technologies is essential for effectively deploying and securing smart devices in both home and business settings.
Looking ahead, advancements in areas like AI and energy efficiency will drive innovation and expand the possibilities of what smart devices can do. As these devices become increasingly integral to our daily lives, it will be more important than ever for IT professionals to stay up-to-date on the latest smart device technologies and best practices.
Fundamental networking and troubleshooting is essential if you are responsible for maintaining a secure environment that works properly while maintaining operational security on your network.
Want to learn more about working with smart devices? Consider our CompTIA Network+ training!
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.